Application Scenarios
You can use functions provided by A-Tune through the CLI client atune-adm. This chapter describes the functions and usage of the A-Tune client.
- Application Scenarios
Overview
Run A-Tune as the root user.
You can run the atune-adm help/--help/-h command to query commands supported by atune-adm.
All example commands are used in single-node mode. For distributed mode, specify an IP address and port number. For example:
# atune-adm -a 192.168.3.196 -p 60001 listThe define, update, undefine, collection, train, and upgrade commands do not support remote execution.
In the command format, brackets ([]) indicate that the parameter is optional, and angle brackets (<>) indicate that the parameter is mandatory. The actual parameters prevail.
Querying Workload Types
list
Function
Query the supported profiles and the values of Active.
Format
atune-adm list
Example
# atune-adm list
Support profiles:
+------------------------------------------------+-----------+
| ProfileName | Active |
+================================================+===========+
| arm-native-android-container-robox | false |
+------------------------------------------------+-----------+
| basic-test-suite-euleros-baseline-fio | false |
+------------------------------------------------+-----------+
| basic-test-suite-euleros-baseline-lmbench | false |
+------------------------------------------------+-----------+
| basic-test-suite-euleros-baseline-netperf | false |
+------------------------------------------------+-----------+
| basic-test-suite-euleros-baseline-stream | false |
+------------------------------------------------+-----------+
| basic-test-suite-euleros-baseline-unixbench | false |
+------------------------------------------------+-----------+
| basic-test-suite-speccpu-speccpu2006 | false |
+------------------------------------------------+-----------+
| basic-test-suite-specjbb-specjbb2015 | false |
+------------------------------------------------+-----------+
| big-data-hadoop-hdfs-dfsio-hdd | false |
+------------------------------------------------+-----------+
| big-data-hadoop-hdfs-dfsio-ssd | false |
+------------------------------------------------+-----------+
| big-data-hadoop-spark-bayesian | false |
+------------------------------------------------+-----------+
| big-data-hadoop-spark-kmeans | false |
+------------------------------------------------+-----------+
| big-data-hadoop-spark-sql1 | false |
+------------------------------------------------+-----------+
| big-data-hadoop-spark-sql10 | false |
+------------------------------------------------+-----------+
| big-data-hadoop-spark-sql2 | false |
+------------------------------------------------+-----------+
| big-data-hadoop-spark-sql3 | false |
+------------------------------------------------+-----------+
| big-data-hadoop-spark-sql4 | false |
+------------------------------------------------+-----------+
| big-data-hadoop-spark-sql5 | false |
+------------------------------------------------+-----------+
| big-data-hadoop-spark-sql6 | false |
+------------------------------------------------+-----------+
| big-data-hadoop-spark-sql7 | false |
+------------------------------------------------+-----------+
| big-data-hadoop-spark-sql8 | false |
+------------------------------------------------+-----------+
| big-data-hadoop-spark-sql9 | false |
+------------------------------------------------+-----------+
| big-data-hadoop-spark-tersort | false |
+------------------------------------------------+-----------+
| big-data-hadoop-spark-wordcount | false |
+------------------------------------------------+-----------+
| cloud-compute-kvm-host | false |
+------------------------------------------------+-----------+
| database-mariadb-2p-tpcc-c3 | false |
+------------------------------------------------+-----------+
| database-mariadb-4p-tpcc-c3 | false |
+------------------------------------------------+-----------+
| database-mongodb-2p-sysbench | false |
+------------------------------------------------+-----------+
| database-mysql-2p-sysbench-hdd | false |
+------------------------------------------------+-----------+
| database-mysql-2p-sysbench-ssd | false |
+------------------------------------------------+-----------+
| database-postgresql-2p-sysbench-hdd | false |
+------------------------------------------------+-----------+
| database-postgresql-2p-sysbench-ssd | false |
+------------------------------------------------+-----------+
| default-default | false |
+------------------------------------------------+-----------+
| docker-mariadb-2p-tpcc-c3 | false |
+------------------------------------------------+-----------+
| docker-mariadb-4p-tpcc-c3 | false |
+------------------------------------------------+-----------+
| hpc-gatk4-human-genome | false |
+------------------------------------------------+-----------+
| in-memory-database-redis-redis-benchmark | false |
+------------------------------------------------+-----------+
| middleware-dubbo-dubbo-benchmark | false |
+------------------------------------------------+-----------+
| storage-ceph-vdbench-hdd | false |
+------------------------------------------------+-----------+
| storage-ceph-vdbench-ssd | false |
+------------------------------------------------+-----------+
| virtualization-consumer-cloud-olc | false |
+------------------------------------------------+-----------+
| virtualization-mariadb-2p-tpcc-c3 | false |
+------------------------------------------------+-----------+
| virtualization-mariadb-4p-tpcc-c3 | false |
+------------------------------------------------+-----------+
| web-apache-traffic-server-spirent-pingpo | false |
+------------------------------------------------+-----------+
| web-nginx-http-long-connection | true |
+------------------------------------------------+-----------+
| web-nginx-https-short-connection | false |
+------------------------------------------------+-----------+
NOTE:
If the value of Active is true, the profile is activated. In the example, the web-nginx-http-long-connection profile is activated.
Workload Type Analysis and Auto Tuning
analysis
Function
Collect real-time statistics from the system to identify and automatically tune workload types.
Format
atune-adm analysis [OPTIONS]
Parameter Description
Example
Use the default model to identify applications.
# atune-adm analysis --characterizationUse the default model to identify applications and perform automatic tuning.
# atune-adm analysisUse the user-defined training model to identify applications.
# atune-adm analysis --model /usr/libexec/atuned/analysis/models/new-model.m
User-defined Model
A-Tune allows users to define and learn new models. To define a new model, perform the following steps:
- Run the define command to define a new profile.
- Run the collection command to collect the system data corresponding to the application.
- Run the train command to train the model.
define
Function
Add a user-defined application scenario and the corresponding profile tuning items.
Format
atune-adm define <service_type> <application_name> <scenario_name> <profile_path>
Example
Add a profile whose service_type is test_service, application_name is test_app, scenario_name is test_scenario, and the tuning item configuration file is example.conf.
# atune-adm define test_service test_app test_scenario ./example.conf
The example.conf file can be written as follows (the following tuning items are optional and are for reference only). You can also run the atune-adm info command to view how the existing profile is written.
[main]
# list its parent profile
[kernel_config]
# to change the kernel config
[bios]
# to change the bios config
[bootloader.grub2]
# to change the grub2 config
[sysfs]
# to change the /sys/* config
[systemctl]
# to change the system service status
[sysctl]
# to change the /proc/sys/* config
[script]
# the script extension of cpi
[ulimit]
# to change the resources limit of user
[schedule_policy]
# to change the schedule policy
[check]
# check the environment
[tip]
# the recommended optimization, which should be performed manually
collection
Function
Collect the global resource usage and OS status during service running and save the collected information to a CSV output file as the input dataset for model training.
NOTE:
- This command depends on the sampling tools such as perf, mpstat, vmstat, iostat, and sar.
- Currently, only the Kunpeng 920 processor is supported. You can run the dmidecode -t processor command to check the CPU model.
Format
atune-adm collection <OPTIONS>
Parameter Description
OPTIONS
Example
# atune-adm collection --filename name --interval 5 --duration 1200 --output_path /home/data --disk sda --network eth0 --app_type test_type
train
Function
Use the collected data to train the model. Collect data of at least two application types during training. Otherwise, an error is reported.
Format
atune-adm train <OPTIONS>
Parameter Description
- OPTIONS
Parameter Description --data_path, -d Path for storing CSV files required for model training --output_file, -o A new model generated during training
Example
Use the CSV file in the data directory as the training input. The generated model new-model.m is stored in the model directory.
# atune-adm train --data_path /home/data --output_file /usr/libexec/atuned/analysis/models/new-model.m
undefine
Function
Delete a user-defined profile.
Format
atune-adm undefine <profile>
Example
Delete the user-defined profile.
# atune-adm undefine test_service-test_app-test_scenario
Querying Profiles
info
Function
View the profile content.
Format
atune-adm info <profile>
Example
View the profile content of web-nginx-http-long-connection.
# atune-adm info web-nginx-http-long-connection
*** web-nginx-http-long-connection:
#
# nginx http long connection A-Tune configuration
#
[main]
include = default-default
[kernel_config]
#TODO CONFIG
[bios]
#TODO CONFIG
[bootloader.grub2]
iommu.passthrough = 1
[sysfs]
#TODO CONFIG
[systemctl]
sysmonitor = stop
irqbalance = stop
[sysctl]
fs.file-max = 6553600
fs.suid_dumpable = 1
fs.aio-max-nr = 1048576
kernel.shmmax = 68719476736
kernel.shmall = 4294967296
kernel.shmmni = 4096
kernel.sem = 250 32000 100 128
net.ipv4.tcp_tw_reuse = 1
net.ipv4.tcp_syncookies = 1
net.ipv4.ip_local_port_range = 1024 65500
net.ipv4.tcp_max_tw_buckets = 5000
net.core.somaxconn = 65535
net.core.netdev_max_backlog = 262144
net.ipv4.tcp_max_orphans = 262144
net.ipv4.tcp_max_syn_backlog = 262144
net.ipv4.tcp_timestamps = 0
net.ipv4.tcp_synack_retries = 1
net.ipv4.tcp_syn_retries = 1
net.ipv4.tcp_fin_timeout = 1
net.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_time = 60
net.ipv4.tcp_mem = 362619 483495 725238
net.ipv4.tcp_rmem = 4096 87380 6291456
net.ipv4.tcp_wmem = 4096 16384 4194304
net.core.wmem_default = 8388608
net.core.rmem_default = 8388608
net.core.rmem_max = 16777216
net.core.wmem_max = 16777216
[script]
prefetch = off
ethtool = -X {network} hfunc toeplitz
[ulimit]
{user}.hard.nofile = 102400
{user}.soft.nofile = 102400
[schedule_policy]
#TODO CONFIG
[check]
#TODO CONFIG
[tip]
SELinux provides extra control and security features to linux kernel. Disabling SELinux will improve the performance but may cause security risks. = kernel
disable the nginx log = application
Updating Profiles
You can update the existing profiles as required.
update
Function
Update the original tuning items in the existing profiles to the content in the new.conf file.
Format
atune-adm update <profile> <profile_path>
Example
Change the tuning item of the profile named test_service-test_app-test_scenario to new.conf.
# atune-adm update test_service-test_app-test_scenario ./new.conf
Activating Profiles
profile
Function
Manually activate a profile to make it in the active state.
Format
atune-adm profile <profile>
Parameter Description
For details about the profile name, see the query result of the list command.
Example
Activate the profile corresponding to web-nginx-http-long-connection.
# atune-adm profile web-nginx-http-long-connection
Rolling Back Profiles
rollback
Functions
Roll back the current configuration to the initial configuration of the system.
Format
atune-adm rollback
Example
# atune-adm rollback
Updating Database
upgrade
Function
Update the system database.
Format
atune-adm upgrade <DB_FILE>
Parameter Description
DB_FILE
New database file path.
Example
Update the dataset to new_sqlite.db.
# atune-adm upgrade ./new_sqlite.db
Querying System Information
check
Function
Check the CPU, BIOS, OS, and NIC information.
Format
atune-adm check
Example
# atune-adm check
cpu information:
cpu:0 version: Kunpeng 920-6426 speed: 2600000000 HZ cores: 64
cpu:1 version: Kunpeng 920-6426 speed: 2600000000 HZ cores: 64
system information:
DMIBIOSVersion: 0.59
OSRelease: 4.19.36-vhulk1906.3.0.h356.eulerosv2r8.aarch64
network information:
name: eth0 product: HNS GE/10GE/25GE RDMA Network Controller
name: eth1 product: HNS GE/10GE/25GE Network Controller
name: eth2 product: HNS GE/10GE/25GE RDMA Network Controller
name: eth3 product: HNS GE/10GE/25GE Network Controller
name: eth4 product: HNS GE/10GE/25GE RDMA Network Controller
name: eth5 product: HNS GE/10GE/25GE Network Controller
name: eth6 product: HNS GE/10GE/25GE RDMA Network Controller
name: eth7 product: HNS GE/10GE/25GE Network Controller
name: docker0 product:
Performing Automatic Parameter Tuning
A-Tune provides the automatic search capability with the optimal configuration, saving the trouble of manually configuring parameters and performance evaluation. This greatly improves the search efficiency of optimal configurations.
tuning
Function
Use the specified project file to search the dynamic space for parameters and find the optimal solution under the current environment configuration.
Format
atune-adm tuning [OPTIONS] <PROJECT_YAML>
NOTE:
Before running the command, ensure that the following conditions are met:
- The YAML configuration file on the server has been edited and stored in the /etc/atuned/tuning/ directory of the atuned service.
- The YAML configuration file on the client has been edited and stored on the atuned client.
Parameter Description
OPTIONS
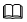 NOTE:
NOTE:
If this parameter is used, the -p parameter must be followed by a specific project name and the YAML file of the project must be specified.- PROJECT_YAML: YAML configuration file of the client.
Configuration Description
Table 1 YAML file on the server
Maximum number of optimization iterations, which is used to limit the number of iterations on the client. Generally, the more optimization iterations, the better the optimization effect, but the longer the time required. Set this parameter based on the site requirements.
Parameters to be optimized and related information.
For details about the object configuration items, see Table 2.
Table 2 Description of object configuration items
Table 3 Description of configuration items of a YAML file on the client
Project name, which must be the same as that in the configuration file on the server.
Parameter search algorithm, which is used to select important parameters. This parameter is optional.
Parameter search cycles, which is used to select important parameters. This parameter is used together with feature_filter_engine.
Number of iterations for each cycle of parameter search, which is used to select important parameters. This parameter is used together with feature_filter_engine.
Number of evenly selected parameters in the value range of tuning parameters, which is used to select important parameters. This parameter is used together with feature_filter_engine.
Performance test evaluation index.
For details about the evaluations configuration items, see Table 4.
Table 4 Description of evaluations configuration item
A positive or negative type of the evaluation result. The value positive indicates that the performance value is minimized, and the value negative indicates that the performance value is maximized.
Example
The following is an example of the YAML file configuration on a server:
project: "compress" maxiterations: 500 startworkload: "" stopworkload: "" object : - name : "compressLevel" info : desc : "The compresslevel parameter is an integer from 1 to 9 controlling the level of compression" get : "cat /root/A-Tune/examples/tuning/compress/compress.py | grep 'compressLevel=' | awk -F '=' '{print $2}'" set : "sed -i 's/compressLevel=\\s*[0-9]*/compressLevel=$value/g' /root/A-Tune/examples/tuning/compress/compress.py" needrestart : "false" type : "continuous" scope : - 1 - 9 dtype : "int" - name : "compressMethod" info : desc : "The compressMethod parameter is a string controlling the compression method" get : "cat /root/A-Tune/examples/tuning/compress/compress.py | grep 'compressMethod=' | awk -F '=' '{print $2}' | sed 's/\"//g'" set : "sed -i 's/compressMethod=\\s*[0-9,a-z,\"]*/compressMethod=\"$value\"/g' /root/A-Tune/examples/tuning/compress/compress.py" needrestart : "false" type : "discrete" options : - "bz2" - "zlib" - "gzip" dtype : "string"The following is an example of the YAML file configuration on a client:
project: "compress" engine : "gbrt" iterations : 20 random_starts : 10 benchmark : "python3 /root/A-Tune/examples/tuning/compress/compress.py" evaluations : - name: "time" info: get: "echo '$out' | grep 'time' | awk '{print $3}'" type: "positive" weight: 20 - name: "compress_ratio" info: get: "echo '$out' | grep 'compress_ratio' | awk '{print $3}'" type: "negative" weight: 80Example
Perform tuning.
# atune-adm tuning --project compress --detail compress_client.yamlRestore the initial configuration before tuning. The compress is the project name in the YAML file.
# atune-adm tuning --restore --project compress










