Installing and Deploying an HA Cluster
This section describes how to install and deploy an HA cluster.
Installation and Deployment
Preparing the Environment
At least two physical machines or virtual machines (VMs) installed with openEuler 21.03 are required. This section uses two physical machines or VMs as an example. For details about how to install openEuler 21.03, see the installation guide.
Modifying the Host Name and the /etc/hosts File
Note: You need to perform the following operations on both hosts. The following uses one host as an example. The IP address used in this section is for reference only.
Before using the HA software, ensure that the host name has been changed and all host names have been written into the /etc/hosts file.
Run the following command to change the host name:
hostnamectl set-hostname ha1Edit the
/etc/hostsfile and write the following fields:172.30.30.65 ha1 172.30.30.66 ha2
Configuring the Yum Source
After the system is successfully installed, the Yum source is configured by default. The file location is stored in the /etc/yum.repos.d/openEuler.repo file. The HA software package uses the following sources:
[OS]
name=OS
baseurl=http://repo.openeuler.org/openEuler-20.03-LTS-SP1/OS/$basearch/
enabled=1
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=http://repo.openeuler.org/openEuler-20.03-LTS-SP1/OS/$basearch/RPM-GPG-KEY-openEuler
[everything]
name=everything
baseurl=http://repo.openeuler.org/openEuler-20.03-LTS-SP1/everything/$basearch/
enabled=1
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=http://repo.openeuler.org/openEuler-20.03-LTS-SP1/everything/$basearch/RPM-GPG-KEY-openEuler
[EPOL]
name=EPOL
baseurl=http://repo.openeuler.org/openEuler-20.03-LTS-SP1/EPOL/$basearch/
enabled=1
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=http://repo.openeuler.org/openEuler-20.03-LTS-SP1/OS/$basearch/RPM-GPG-KEY-openEuler
Installing the Components of the HA Software Package
yum install -y corosync pacemaker pcs fence-agents fence-virt corosync-qdevice sbd drbd drbd-utils
Setting the hacluster User Password
passwd hacluster
Modifying the /etc/corosync/corosync.conf file
totem {
version: 2
cluster_name: hacluster
crypto_cipher: none
crypto_hash: none
}
logging {
fileline: off
to_stderr: yes
to_logfile: yes
logfile: /var/log/cluster/corosync.log
to_syslog: yes
debug: on
logger_subsys {
subsys: QUORUM
debug: on
}
}
quorum {
provider: corosync_votequorum
expected_votes: 2
two_node: 1
}
nodelist {
node {
name: ha1
nodeid: 1
ring0_addr: 172.30.30.65
}
node {
name: ha2
nodeid: 2
ring0_addr: 172.30.30.66
}
}
Managing Services
Disabling the Firewall
Run the following command to disable the firewall:
systemctl stop firewalldChange SELinux to disabled in the
/etc/selinux/configfile.# SELINUX=disabled
Managing the pcs Service
Run the following command to start the pcs service:
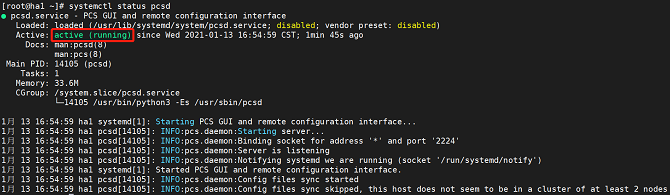
systemctl start pcsdRun the following command to query the pcs service status:
systemctl status pcsdThe service is started successfully if the following information is displayed:
Managing the Pacemaker Service
Run the following command to start the Pacemaker service:
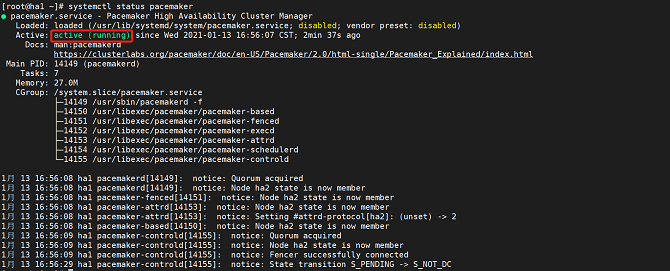
systemctl start pacemakerRun the following command to query the Pacemaker service status:
systemctl status pacemakerThe service is started successfully if the following information is displayed:
Managing the Corosync Service
Run the following command to start the Corosync service:
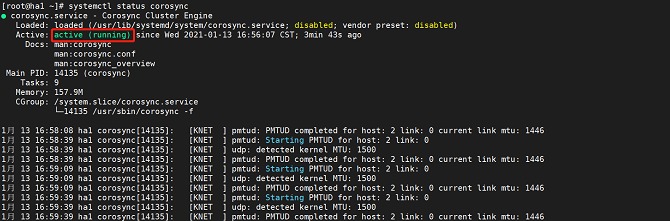
systemctl start corosyncRun the following command to query the Corosync service status:
systemctl status corosyncThe service is started successfully if the following information is displayed:
Performing Node Authentication
Note: Perform this operation on either node.
# Use pcs to authenticate the user names and passwords of each node.
$ pcs host auth ha1 ha2
Username: hacluster
Password:
ha1: Authorized
ha2: Authorized
Accessing the Front-End Management Platform
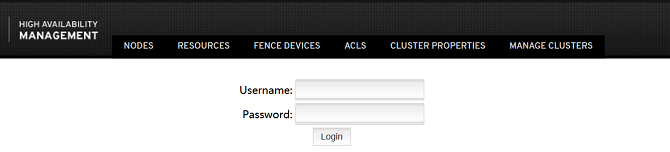
After the preceding services are started, open the browser (Chrome or Firefox is recommended) and enter https://localhost:2224 in the address box.
- The following figure shows the native management platform:
For details about how to install the management platform newly developed by the community, see https://gitee.com/openeuler/ha-api/blob/master/docs/build.md.
- The following is the management platform newly developed by the community:

Note: only the Chinese version is available.










