Using gala-spider
This chapter describes how to deploy and use gala-spider and gala-inference.
gala-spider
gala-spider provides the OS-level topology drawing function. It periodically obtains the data of all observed objects collected by gala-gopher (an OS-level data collection software) at a certain time point and calculates the topology relationship between them. The generated topology is saved to the graph database ArangoDB.
Installation
Mount the Yum sources.
[oe-22.03-lts-sp1-everything] # openEuler 22.03-LTS-SP1 official repository
name=oe-2203-lts-sp1-everything
baseurl=http://repo.openeuler.org/openEuler-22.03-LTS-SP1/everything/x86_64/
enabled=1
gpgcheck=0
priority=1
[oe-22.03-lts-sp1-epol-update] # openEuler 22.03-LTS-SP1 official Update repository
name=oe-22.03-lts-sp1-epol-update
baseurl=http://repo.openeuler.org/openEuler-22.03-LTS-SP1/EPOL/update/main/x86_64/
enabled=1
gpgcheck=0
priority=1
[oe-22.03-lts-sp1-epol-main] # openEuler 22.03-LTS-SP1 official EPOL repository
name=oe-22.03-lts-sp1-epol-main
baseurl=http://repo.openeuler.org/openEuler-22.03-LTS-SP1/EPOL/main/x86_64/
enabled=1
gpgcheck=0
priority=1
Install gala-spider.
yum install gala-spider
Configuration
Configuration File Description
The configuration file of gala-spider is /etc/gala-spider/gala-spider.yaml. The configuration items in this file are described as follows:
global: global configuration information.data_source: database for collecting observation metrics. Currently, onlyprometheusis supported.data_agent: agent for collecting observation metrics. Currently, onlygala_gopheris supported.
spider:log_conf: log configuration information.log_path: log file path.log_level: level of the logs to be printed. The value can beDEBUG,INFO,WARNING,ERROR, orCRITICAL.max_size: log file size, in MB.backup_count: number of backup log files.
storage: configuration information about the topology storage service.period: storage period, in seconds, indicating the interval for storing the topology.database: graph database for storage. Currently, onlyarangodbis supported.db_conf: configuration information of the graph database.url: IP address of the graph database server.db_name: name of the database where the topology is stored.
kafka: Kafka configuration information.server: Kafka server address.metadata_topic: topic name of the observed metadata messages.metadata_group_id: consumer group ID of the observed metadata messages.
prometheus: Prometheus database configuration information.base_url: IP address of the Prometheus server.instant_api: API for collecting data at a single time point.range_api: API for collecting data in a time range.step: collection time step, which is configured forrange_api.
Configuration File Example
global:
data_source: "prometheus"
data_agent: "gala_gopher"
prometheus:
base_url: "http://localhost:9090/"
instant_api: "/api/v1/query"
range_api: "/api/v1/query_range"
step: 1
spider:
log_conf:
log_path: "/var/log/gala-spider/spider.log"
# log level: DEBUG/INFO/WARNING/ERROR/CRITICAL
log_level: INFO
# unit: MB
max_size: 10
backup_count: 10
storage:
# unit: second
period: 60
database: arangodb
db_conf:
url: "http://localhost:8529"
db_name: "spider"
kafka:
server: "localhost:9092"
metadata_topic: "gala_gopher_metadata"
metadata_group_id: "metadata-spider"
Start
Run the following command to start gala-spider.
spider-storageUse the systemd service to start gala-spider.
systemctl start gala-spider
How to Use
Deployment of External Dependent Software
The running of gala-spider depends on multiple external software for interaction. Therefore, before starting gala-spider, you need to deploy the software on which gala-spider depends. The following figure shows the software dependency of gala-spider.
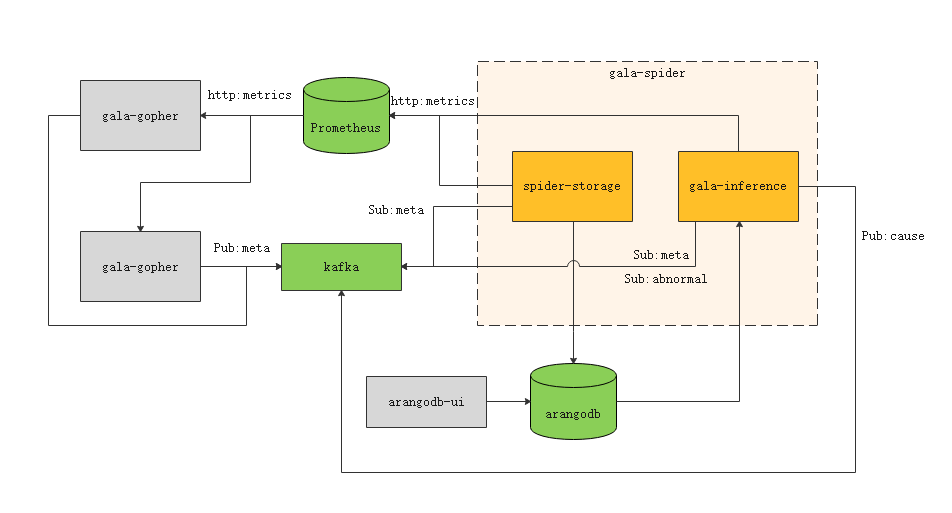
The dotted box on the right indicates the two functional components of gala-spider. The green parts indicate the external components that gala-spider directly depends on, and the gray rectangles indicate the external components that gala-spider indirectly depends on.
- spider-storage: core component of gala-spider, which provides the topology storage function.
- Obtains the metadata of the observation object from Kafka.
- Obtains information about all observation object instances from Prometheus.
- Saves the generated topology to the graph database ArangoDB.
- gala-inference: core component of gala-spider, which provides the root cause locating function. It subscribes to abnormal KPI events from Kafka to trigger the root cause locating process of abnormal KPIs, constructs a fault propagation graph based on the topology obtained from the ArangoDB, and outputs the root cause locating result to Kafka.
- prometheus: time series database. The observation metric data collected by the gala-gopher component is reported to Prometheus for further processing.
- kafka: messaging middleware, which is used to store the observation object metadata reported by gala-gopher, exception events reported by the exception detection component gala-anteater, and root cause locating results reported by the cause-inference component.
- arangodb: graph database, which is used to store the topology generated by spider-storage.
- gala-gopher: data collection component. It must be deployed in advance.
- arangodb-ui: UI provided by ArangoDB, which can be used to query topologies.
The two functional components in gala-spider are released as independent software packages.
spider-storage: corresponds to the gala-spider software package in this section.
gala-inference: corresponds to the gala-inference software package.
For details about how to deploy the gala-gopher software, see Using gala-gopher. This section only describes how to deploy ArangoDB.
The current ArangoDB version is 3.8.7, which has the following requirements on the operating environment:
- Only the x86 system is supported.
- GCC 10 or later
For details about ArangoDB deployment, see Deployment in the ArangoDB official document.
The RPM-based ArangoDB deployment process is as follows:
Configure the Yum sources.
[oe-22.03-lts-sp1-everything] # openEuler 22.03-LTS-SP1 official repository name=oe-2203-lts-sp1-everything baseurl=<http://repo.openeuler.org/openEuler-22.03-LTS-SP1/everything/x86_64/> enabled=1 gpgcheck=0 priority=1 [oe-22.03-lts-sp1-epol-main] # openEuler 22.03-LTS-SP1 official EPOL repository name=oe-22.03-lts-sp1-epol-main baseurl=<http://repo.openeuler.org/openEuler-22.03-LTS-SP1/EPOL/main/x86_64/> enabled=1 gpgcheck=0 priority=1Install arangodb3.
yum install arangodb3Modify the configurations.
The configuration file of the arangodb3 server is /etc/arangodb3/arangod.conf. You need to modify the following configurations:
endpoint: IP address of the arangodb3 server.authentication: whether identity authentication is required for accessing the arangodb3 server. Currently, gala-spider does not support identity authentication. Therefore, setauthenticationtofalse.
The following is an example.
[server] endpoint = tcp://0.0.0.0:8529 authentication = falseStart arangodb3.
systemctl start arangodb3
Modifying gala-spider Configuration Items
After the dependent software is started, you need to modify some configuration items in the gala-spider configuration file. The following is an example.
Configure the Kafka server address.
kafka:
server: "localhost:9092"
Configure the Prometheus server address.
prometheus:
base_url: "http://localhost:9090/"
Configure the IP address of the ArangoDB server.
storage:
db_conf:
url: "http://localhost:8529"
Starting the Service
Run systemctl start gala-spider to start the service. Run systemctl status gala-spider to check the startup status. If the following information is displayed, the startup is successful:
$ systemctl status gala-spider
● gala-spider.service - a-ops gala spider service
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/gala-spider.service; enabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since Tue 2022-08-30 17:28:38 CST; 1 day 22h ago
Main PID: 2263793 (spider-storage)
Tasks: 3 (limit: 98900)
Memory: 44.2M
CGroup: /system.slice/gala-spider.service
└─2263793 /usr/bin/python3 /usr/bin/spider-storage
Output Example
You can query the topology generated by gala-spider on the UI provided by ArangoDB. The procedure is as follows:
Enter the IP address of the ArangoDB server in the address box of the browser, for example, http://localhost:8529. The ArangoDB UI is displayed.
Click DB in the upper right corner of the page to switch to the spider database.
On the COLLECTIONS page, you can view the collections of observation object instances and topology relationships stored in different time segments, as shown in the following figure.
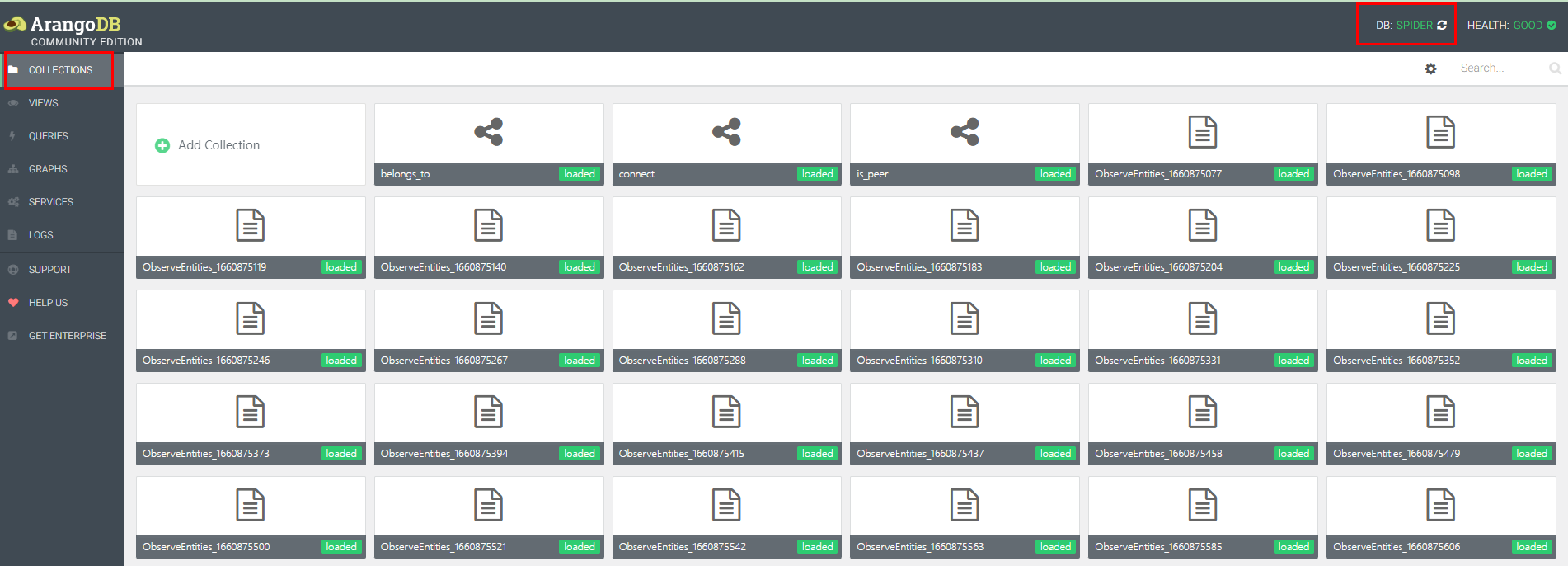
You can query the stored topology using the AQL statements provided by ArangoDB. For details, see the AQL Documentation.
gala-inference
gala-inference provides the capability of locating root causes of abnormal KPIs. It uses the exception detection result and topology as the input and outputs the root cause locating result to Kafka. The gala-inference component is archived in the gala-spider project.
Installation
Mount the Yum sources.
[oe-22.03-lts-sp1-everything] # openEuler 22.03-LTS-SP1 officially released repository
name=oe-2203-lts-sp1-everything
baseurl=http://repo.openeuler.org/openEuler-22.03-LTS-SP1/everything/x86_64/
enabled=1
gpgcheck=0
priority=1
[oe-22.03-lts-sp1-epol-update] # openEuler 22.03-LTS-SP1 Update officially released repository
name=oe-22.03-lts-sp1-epol-update
baseurl=http://repo.openeuler.org/openEuler-22.03-LTS-SP1/EPOL/update/main/x86_64/
enabled=1
gpgcheck=0
priority=1
[oe-22.03-lts-sp1-epol-main] # openEuler 22.03-LTS-SP1 EPOL officially released repository
name=oe-22.03-lts-sp1-epol-main
baseurl=http://repo.openeuler.org/openEuler-22.03-LTS-SP1/EPOL/main/x86_64/
enabled=1
gpgcheck=0
priority=1
Install gala-inference.
yum install gala-inference
Configuration
Configuration File Description
The configuration items in the gala-inference configuration file /etc/gala-inference/gala-inference.yaml are described as follows:
inference: configuration information about the root cause locating algorithm.tolerated_bias: tolerable time offset for querying the topology at the exception time point, in seconds.topo_depth: maximum depth for topology query.root_topk: yop K root cause metrics generated in the root cause locating result.infer_policy: root cause derivation policy, which can bedfsorrw.sample_duration: sampling period of historical metric data, in seconds.evt_valid_duration: valid period of abnormal system metric events during root cause locating, in seconds.evt_aging_duration: aging period of abnormal metric events during root cause locating, in seconds.
kafka: Kafka configuration information.server: IP address of the Kafka server.metadata_topic: configuration information about the observed metadata messages.topic_id: topic name of the observed metadata messages.group_id: consumer group ID of the observed metadata messages.
abnormal_kpi_topic: configuration information about abnormal KPI event messages.topic_id: topic name of the abnormal KPI event messages.group_id: consumer group ID of the abnormal KPI event messages.
abnormal_metric_topic: configuration information about abnormal metric event messages.topic_id: topic name of the abnormal metric event messages.group_id: consumer group ID of the abnormal system metric event messages.consumer_to: timeout interval for consuming abnormal system metric event messages, in seconds.
inference_topic: configuration information about the output event messages of the root cause locating result.topic_id: topic name of the output event messages of the root cause locating result.
arangodb: configuration information about the ArangoDB graph database, which is used to query sub-topologies required for root cause locating.url: IP address of the graph database server.db_name: name of the database where the topology is stored.
log_conf: log configuration information.log_path: log file path.log_level: level of the logs to be printed. The value can beDEBUG,INFO,WARNING,ERROR, orCRITICAL.max_size: log file size, in MB.backup_count: number of backup log files.
prometheus: Prometheus database configuration information, which is used to obtain historical time series data of metrics.base_url: IP address of the Prometheus server.range_api: API for collecting data in a time range.step: collection time step, which is configured forrange_api.
Configuration File Example
inference:
# Tolerable time offset for querying the topology at the exception time point, in seconds.
tolerated_bias: 120
topo_depth: 10
root_topk: 3
infer_policy: "dfs"
# Unit: second
sample_duration: 600
# Valid period of abnormal metric events during root cause locating, in seconds.
evt_valid_duration: 120
# Aging period of abnormal metric events, in seconds.
evt_aging_duration: 600
kafka:
server: "localhost:9092"
metadata_topic:
topic_id: "gala_gopher_metadata"
group_id: "metadata-inference"
abnormal_kpi_topic:
topic_id: "gala_anteater_hybrid_model"
group_id: "abn-kpi-inference"
abnormal_metric_topic:
topic_id: "gala_anteater_metric"
group_id: "abn-metric-inference"
consumer_to: 1
inference_topic:
topic_id: "gala_cause_inference"
arangodb:
url: "http://localhost:8529"
db_name: "spider"
log:
log_path: "/var/log/gala-inference/inference.log"
# log level: DEBUG/INFO/WARNING/ERROR/CRITICAL
log_level: INFO
# unit: MB
max_size: 10
backup_count: 10
prometheus:
base_url: "http://localhost:9090/"
range_api: "/api/v1/query_range"
step: 5
Start
Run the following command to start gala-inference.
gala-inferenceUse the systemd service to start gala-inference.
systemctl start gala-inference
How to Use
Dependent Software Deployment
The running dependency of gala-inference is the same as that of gala-spider. For details, see Deployment of External Dependent Software. In addition, gala-inference indirectly depends on the running of gala-spider and gala-anteater. Deploy gala-spider and gala-anteater in advance.
Modify configuration items
Modify some configuration items in the gala-inference configuration file. The following is an example.
Configure the Kafka server address.
kafka:
server: "localhost:9092"
Configure the Prometheus server address.
prometheus:
base_url: "http://localhost:9090/"
Configure the IP address of the ArangoDB server.
arangodb:
url: "http://localhost:8529"
Starting the Service
Run systemctl start gala-inference to start the service. Run systemctl status gala-inference to check the startup status. If the following information is displayed, the startup is successful:
$ systemctl status gala-inference
● gala-inference.service - a-ops gala inference service
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/gala-inference.service; enabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since Tue 2022-08-30 17:55:33 CST; 1 day 22h ago
Main PID: 2445875 (gala-inference)
Tasks: 10 (limit: 98900)
Memory: 48.7M
CGroup: /system.slice/gala-inference.service
└─2445875 /usr/bin/python3 /usr/bin/gala-inference
Output Example
When the exception detection module gala-anteater detects a KPI exception, it exports the corresponding abnormal KPI event to Kafka. The gala-inference keeps monitoring the message of the abnormal KPI event. If gala-inference receives the message of the abnormal KPI event, root cause locating is triggered. The root cause locating result is exported to Kafka. You can view the root cause locating result on the Kafka server. The basic procedure is as follows:
If Kafka is installed using the source code, go to the Kafka installation directory.
cd /root/kafka_2.13-2.8.0Run the command for consuming the topic to obtain the output of root cause locating.
./bin/kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --topic gala_cause_inferenceOutput example:
{ "Timestamp": 1661853360000, "event_id": "1661853360000_1fd37742xxxx_sli_12154_19", "Atrributes": { "event_id": "1661853360000_1fd37742xxxx_sli_12154_19" }, "Resource": { "abnormal_kpi": { "metric_id": "gala_gopher_sli_rtt_nsec", "entity_id": "1fd37742xxxx_sli_12154_19", "timestamp": 1661853360000, "metric_labels": { "machine_id": "1fd37742xxxx", "tgid": "12154", "conn_fd": "19" } }, "cause_metrics": [ { "metric_id": "gala_gopher_proc_write_bytes", "entity_id": "1fd37742xxxx_proc_12154", "metric_labels": { "__name__": "gala_gopher_proc_write_bytes", "cmdline": "/opt/redis/redis-server x.x.x.172:3742", "comm": "redis-server", "container_id": "5a10635e2c43", "hostname": "openEuler", "instance": "x.x.x.172:8888", "job": "prometheus", "machine_id": "1fd37742xxxx", "pgid": "12154", "ppid": "12126", "tgid": "12154" }, "timestamp": 1661853360000, "path": [ { "metric_id": "gala_gopher_proc_write_bytes", "entity_id": "1fd37742xxxx_proc_12154", "metric_labels": { "__name__": "gala_gopher_proc_write_bytes", "cmdline": "/opt/redis/redis-server x.x.x.172:3742", "comm": "redis-server", "container_id": "5a10635e2c43", "hostname": "openEuler", "instance": "x.x.x.172:8888", "job": "prometheus", "machine_id": "1fd37742xxxx", "pgid": "12154", "ppid": "12126", "tgid": "12154" }, "timestamp": 1661853360000 }, { "metric_id": "gala_gopher_sli_rtt_nsec", "entity_id": "1fd37742xxxx_sli_12154_19", "metric_labels": { "machine_id": "1fd37742xxxx", "tgid": "12154", "conn_fd": "19" }, "timestamp": 1661853360000 } ] } ] }, "SeverityText": "WARN", "SeverityNumber": 13, "Body": "A cause inferring event for an abnormal event" }










