System Resource Management
The libvirt command manages VM system resources, such as vCPU and virtual memory resources.
Before you start:
- Ensure that the libvirtd daemon is running on the host.
- Run the virsh list --all command to check that the VM has been defined.
Managing vCPU
CPU Shares
Overview
In a virtualization environment, multiple VMs on the same host compete for physical CPUs. To prevent some VMs from occupying too many physical CPU resources and affecting the performance of other VMs on the same host, you need to balance the vCPU scheduling of VMs to prevent excessive competition for physical CPUs.
The CPU share indicates the total capability of a VM to compete for physical CPU computing resources. You can set cpu_shares to specify the VM capacity to preempt physical CPU resources. The value of cpu_shares is a relative value without a unit. The CPU computing resources obtained by a VM are the available computing resources of physical CPUs (excluding reserved CPUs) allocated to VMs based on the CPU shares. Adjust the CPU shares to ensure the service quality of VM CPU computing resources.
Procedure
Change the value of cpu_shares allocated to the VM to balance the scheduling between vCPUs.
Check the current CPU share of the VM.
# virsh schedinfo <VMInstance> Scheduler : posix cpu_shares : 1024 vcpu_period : 100000 vcpu_quota : -1 emulator_period: 100000 emulator_quota : -1 global_period : 100000 global_quota : -1 iothread_period: 100000 iothread_quota : -1Online modification: Run the virsh schedinfo command with the --live parameter to modify the CPU share of a running VM.
# virsh schedinfo <VMInstance> --live cpu_shares=<number>For example, to change the CPU share of the running openEulerVM from 1024 to 2048, run the following commands:
# virsh schedinfo openEulerVM --live cpu_shares=2048 Scheduler : posix cpu_shares : 2048 vcpu_period : 100000 vcpu_quota : -1 emulator_period: 100000 emulator_quota : -1 global_period : 100000 global_quota : -1 iothread_period: 100000 iothread_quota : -1The modification of the cpu_shares value takes effect immediately. The running time of the openEulerVM is twice the original running time. However, the modification will become invalid after the VM is shut down and restarted.
Permanent modification: Run the virsh schedinfo command with the --config parameter to change the CPU share of the VM in the libvirt internal configuration.
# virsh schedinfo <VMInstance> --config cpu_shares=<number>For example, run the following command to change the CPU share of openEulerVM from 1024 to 2048:
# virsh schedinfo openEulerVM --config cpu_shares=2048 Scheduler : posix cpu_shares : 2048 vcpu_period : 0 vcpu_quota : 0 emulator_period: 0 emulator_quota : 0 global_period : 0 global_quota : 0 iothread_period: 0 iothread_quota : 0The modification on cpu_shares does not take effect immediately. Instead, the modification takes effect after the openEulerVM is started next time and takes effect permanently. The running time of the openEulerVM is twice that of the original VM.
Binding the QEMU Process to a Physical CPU
Overview
You can bind the QEMU main process to a specific physical CPU range, ensuring that VMs running different services do not interfere with adjacent VMs. For example, in a typical cloud computing scenario, multiple VMs run on one physical machine, and they carry diversified services, causing different degrees of resource occupation. To avoid interference of a VM with dense-storage I/O to an adjacent VM, storage processes that process I/O of different VMs need to be completely isolated. The QEMU main process handles frontend and backend services. Therefore, isolation needs to be implemented.
Procedure
Run the virsh emulatorpin command to bind the QEMU main process to a physical CPU.
Check the range of the physical CPU bound to the QEMU process:
# virsh emulatorpin openEulerVM emulator: CPU Affinity ---------------------------------- *: 0-63This indicates that the QEMU main process corresponding to VM openEulerVM can be scheduled on all physical CPUs of the host.
Online binding: Run the vcpu emulatorpin command with the --live parameter to modify the binding relationship between the QEMU process and the running VM.
# virsh emulatorpin openEulerVM --live 2-3 # virsh emulatorpin openEulerVM emulator: CPU Affinity ---------------------------------- *: 2-3The preceding commands bind the QEMU process corresponding to VM openEulerVM to physical CPUs 2 and 3. That is, the QEMU process is scheduled only on the two physical CPUs. The binding relationship takes effect immediately but becomes invalid after the VM is shut down and restarted.
Permanent binding: Run the virsh emulatorpin command with the --config parameter to modify the binding relationship between the VM and the QEMU process in the libvirt internal configuration.
# virsh emulatorpin openEulerVM --config 0-3,^1 # virsh emulatorpin euler emulator: CPU Affinity ---------------------------------- *: 0,2-3The preceding commands bind the QEMU process corresponding to VM openEulerVM to physical CPUs 0, 2 and 3. That is, the QEMU process is scheduled only on the three physical CPUs. The modification of the binding relationship does not take effect immediately. Instead, the modification takes effect after the next startup of the VM and takes effect permanently.
Adjusting the vCPU Binding Relationship
Overview
The vCPU of a VM is bound to a physical CPU. That is, the vCPU is scheduled only on the bound physical CPU to improve VM performance in specific scenarios. For example, in a NUMA system, vCPUs are bound to the same NUMA node to prevent cross-node memory access and VM performance deterioration. If the vCPU is not bound, by default, the vCPU can be scheduled on any physical CPU. The specific binding policy is determined by the user.
Procedure
Run the virsh vcpupin command to adjust the binding relationship between vCPUs and physical CPUs.
View the vCPU binding information of the VM.
# virsh vcpupin openEulerVM VCPU CPU Affinity ---------------------- 0 0-63 1 0-63 2 0-63 3 0-63This indicates that all vCPUs of VM openEulerVM can be scheduled on all physical CPUs of the host.
Online adjustment: Run the vcpu vcpupin command with the --live parameter to modify the vCPU binding relationship of a running VM.
# virsh vcpupin openEulerVM --live 0 2-3 # virsh vcpupin euler VCPU CPU Affinity ---------------------- 0 2-3 1 0-63 2 0-63 3 0-63The preceding commands bind vCPU 0 of VM openEulerVM to pCPU 2 and pCPU 3. That is, vCPU 0 is scheduled only on the two physical CPUs. The binding relationship takes effect immediately but becomes invalid after the VM is shut down and restarted.
Permanent adjustment: Run the virsh vcpupin command with the --config parameter to modify the vCPU binding relationship of the VM in the libvirt internal configuration.
# virsh vcpupin openEulerVM --config 0 0-3,^1 # virsh vcpupin openEulerVM VCPU CPU Affinity ---------------------- 0 0,2-3 1 0-63 2 0-63 3 0-63The preceding commands bind vCPU 0 of VM openEulerVM to physical CPUs 0, 2, and 3. That is, vCPU 0 is scheduled only on the three physical CPUs. The modification of the binding relationship does not take effect immediately. Instead, the modification takes effect after the next startup of the VM and takes effect permanently.
CPU Hot Add
Overview
This feature allows users to hot add CPUs to a running VM without affecting its normal running. When the internal service pressure of a VM keeps increasing, all CPUs will be overloaded. To improve the computing capability of the VM, you can use the CPU hot add function to increase the number of CPUs on the VM without stopping it.
Constraints
- For processors using the AArch64 architecture, the specified VM chipset type (machine) needs to be virt-4.1 or a later version when a VM is created. For processors using the x86_64 architecture, the specified VM chipset type (machine) needs to be pc-i440fx-1.5 or a later version when a VM is created.
- When configuring Guest NUMA, you need to configure the vCPUs that belong to the same socket in the same vNode. Otherwise, the VM may be soft locked up after the CPU is hot added, which may cause the VM panic.
- VMs do not support CPU hot add during migration, hibernation, wake-up, or snapshot.
- Whether the hot added CPU can automatically go online depends on the VM OS logic rather than the virtualization layer.
- CPU hot add is restricted by the maximum number of CPUs supported by the Hypervisor and GuestOS.
- When a VM is being started, stopped, or restarted, the hot added CPU may become invalid. However, the hot added CPU takes effect after the VM is restarted.
- During VM CPU hot add, if the number of added CPUs is not an integer multiple of the number of cores in the VM CPU topology configuration item, the CPU topology displayed in the VM may be disordered. You are advised to add CPUs whose number is an integer multiple of the number of cores each time.
- If the hot added CPU needs to take effect online and is still valid after the VM is restarted, the --config and --live options need to be transferred to the virsh setvcpus API to persist the hot added CPU.
Procedure
VM XML Configuration
To use the CPU hot add function, configure the number of CPUs, the maximum number of CPUs supported by the VM, and the VM chipset type when creating the VM. (For the AArch64 architecture, the virt-4.1 or a later version is required. For the x86_64 architecture, the pc-i440fx-1.5 or later version is required. The AArch64 VM is used as an example. The configuration template is as follows:
<domain type='kvm'> ... <vcpu placement='static' current='m'>n</vcpu> <os> <type arch='aarch64' machine='virt-4.1'>hvm</type> </os> ... <domain>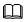 Note
Note- The value of placement must be static.
- m indicates the current number of CPUs on the VM, that is, the default number of CPUs after the VM is started. n indicates the maximum number of CPUs that can be hot added to a VM. The value cannot exceed the maximum CPU specifications supported by the Hypervisor or GuestOS. n is greater than or equal to m.
For example, if the current number of CPUs of a VM is 4 and the maximum number of hot added CPUs is 64, the XML configuration is as follows:
<domain type='kvm'> ... <vcpu placement='static' current='4'>64</vcpu> <os> <type arch='aarch64' machine='virt-4.1'>hvm</type> </os> ...
Hot Adding and Bringing CPUs Online
If the hot added CPU needs to be automatically brought online, create the udev rules file /etc/udev/rules.d/99-hotplug-cpu.rules in the VM as user root and define the udev rules in the file. The following is an example:
### automatically online hot-plugged cpu ACTION=="add", SUBSYSTEM=="cpu", ATTR{online}="1" Note
Note
If you do not use the udev rules, you can use the root permission to manually bring the hot added CPU online by running the following commands:for i in `grep -l 0 /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu*/online` do echo 1 > $i doneUse the virsh tool to hot add CPUs to the VM. For example, to set the number of CPUs after hot adding to 6 on the VM named openEulerVM and make the hot add take effect online, run the following command:
virsh setvcpus openEulerVM 6 --live Note
Note
The format for running the virsh setvcpus command to hot add a VM CPU is as follows:virsh setvcpus <domain> <count> [--config] [--live]- domain: Parameter, which is mandatory. Specifies the name of a VM.
- count: Parameter, which is mandatory. Specifies the number of target CPUs, that is, the number of CPUs after hot adding.
- --config: Option, which is optional. This parameter is still valid when the VM is restarted.
- --live: Option, which is optional. The configuration takes effect online.
Managing Virtual Memory
Introduction to NUMA
Traditional multi-core computing uses the symmetric multi-processor (SMP) mode. Multiple processors are connected to a centralized memory and I/O bus. All processors can access only the same physical memory. Therefore, the SMP system is also referred to as a uniform memory access (UMA) system. Uniformity means that a processor can only maintain or share a unique value for each data record in memory at any time. Obviously, the disadvantage of SMP is its limited scalability, because when the memory and the I/O interface are saturated, adding a processor cannot obtain higher performance.
The non-uniform memory access architecture (NUMA) is a distributed memory access mode. In this mode, a processor can access different memory addresses at the same time, which greatly improves concurrency. With this feature, a processor is divided into multiple nodes, each of which is allocated a piece of local memory space. The processors of all nodes can access all physical memories, but the time required for accessing the memory on the local node is much shorter than that on a remote node.
Configuring Host NUMA
To improve VM performance, you can specify NUMA nodes for a VM using the VM XML configuration file before the VM is started so that the VM memory is allocated to the specified NUMA nodes. This feature is usually used together with the vCPU to prevent the vCPU from remotely accessing the memory.
Procedure
Check the NUMA topology of the host.
# numactl -H available: 4 nodes (0-3) node 0 cpus: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 node 0 size: 31571 MB node 0 free: 17095 MB node 1 cpus: 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 node 1 size: 32190 MB node 1 free: 28057 MB node 2 cpus: 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 node 2 size: 32190 MB node 2 free: 10562 MB node 3 cpus: 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 node 3 size: 32188 MB node 3 free: 272 MB node distances: node 0 1 2 3 0: 10 15 20 20 1: 15 10 20 20 2: 20 20 10 15 3: 20 20 15 10Add the numatune field to the VM XML configuration file to create and start the VM. For example, to allocate NUMA node 0 on the host to the VM, configure parameters as follows:
<numatune> <memory mode="strict" nodeset="0"/> </numatune>If the vCPU of the VM is bound to the physical CPU of node 0, the performance deterioration caused by the vCPU accessing the remote memory can be avoided.
 NOTE:
NOTE:- The sum of memory allocated to the VM cannot exceed the remaining available memory of the NUMA node. Otherwise, the VM may fail to start.
- You are advised to bind the VM memory and vCPU to the same NUMA node to avoid the performance deterioration caused by vCPU access to the remote memory. For example, bind the vCPU to NUMA node 0 as well.
Configuring Guest NUMA
Many service software running on VMs is optimized for the NUMA architecture, especially for large-scale VMs. openEuler provides the Guest NUMA feature to display the NUMA topology in VMs. You can identify the structure to optimize the performance of service software and ensure better service running.
When configuring guest NUMA, you can specify the location of vNode memory on the host to implement memory block binding and vCPU binding so that the vCPU and memory on the vNode are on the same physical NUMA node.
Procedure
After Guest NUMA is configured in the VM XML configuration file, you can view the NUMA topology on the VM. <numa> is mandatory for Guest NUMA.
<cputune>
<vcpupin vcpu='0' cpuset='0-3'/>
<vcpupin vcpu='1' cpuset='0-3'/>
<vcpupin vcpu='2' cpuset='16-19'/>
<vcpupin vcpu='3' cpuset='16-19'/>
</cputune>
<numatune>
<memnode cellid="0" mode="strict" nodeset="0"/>
<memnode cellid="1" mode="strict" nodeset="1"/>
</numatune>
[...]
<cpu>
<numa>
<cell id='0' cpus='0-1' memory='2097152'/>
<cell id='1' cpus='2-3' memory='2097152'/>
</numa>
</cpu>
NOTE:
- <numa> provides the NUMA topology function for VMs. cell id indicates the vNode ID, cpus indicates the vCPU ID, and memory indicates the memory size on the vNode.
- If you want to use Guest NUMA to provide better performance, configure <numatune> and <cputune> so that the vCPU and memory are distributed on the same physical NUMA node.
- cellid in <numatune> corresponds to cell id in <numa>. mode can be set to strict (apply for memory from a specified node strictly. If the memory is insufficient, the application fails.), preferred (apply for memory from a node first. If the memory is insufficient, apply for memory from another node), or interleave (apply for memory from a specified node in cross mode).; nodeset indicates the specified physical NUMA node.
- In <cputune>, you need to bind the vCPU in the same cell id to the physical NUMA node that is the same as the memnode.
Memory Hot Add
Overview
In virtualization scenarios, the memory, CPU, and external devices of VMs are simulated by software. Therefore, the memory can be adjusted online for VMs at the virtualization bottom layer. In the current openEuler version, memory can be added to a VM online. If the physical memory of a VM is insufficient and the VM cannot be shut down, you can use this feature to add physical memory resources to the VM.
Constraints
- For processors using the AArch64 architecture, the specified VM chipset type (machine) needs to be virt-4.1 or a later version when a VM is created.For processors using the x86 architecture, the specified VM chipset type (machine) needs to be a later version than pc-i440fx-1.5 when a VM is created.
- Guest NUMA on which the memory hot add feature depends needs to be configured on the VM. Otherwise, the memory hot add process cannot be completed.
- When hot adding memory, you need to specify the ID of Guest NUMA node to which the new memory belongs. Otherwise, the memory hot add fails.
- The VM kernel should support memory hot add. Otherwise, the VM cannot identify the newly added memory or the memory cannot be brought online.
- For a VM that uses hugepages, the capacity of the hot added memory should be an integral multiple of hugepagesz. Otherwise, the hot add fails.
- The hot added memory size should be an integral multiple of the Guest physical memory block size (block_size_bytes). Otherwise, the VM cannot go online. The value of block_size_bytes can be obtained using the lsmem command in Guest.
- After n pieces of virtio-net NICs are configured, the maximum number of hot add times is set to min{max_slot, 64 - n} to reserve slots for NICs.
- The vhost-user device and the memory hot add feature are mutually exclusive. A VM configured with the vhost-user device does not support memory hot add. After the memory is hot added to a VM, the vhost-user device cannot be hot added.
- If the VM OS is Linux, ensure that the initial memory is greater than or equal to 4 GB.
- If the VM OS is Windows, the first hot added memory needs to be specified to Guest NUMA node0. Otherwise, the hot added memory cannot be identified by the VM.
- In passthrough scenarios, memory needs to be allocated in advance. Therefore, it is normal that the startup and hot add of memory are slower than those of common VMs (especially large-specification VMs).
- It is recommended that the ratio of the available memory to the hot added memory be at least 1:32. That is, at least 1 GB available memory is required for the VM with 32 GB hot added memory. If the ratio is less than 1:32, the VM may be suspended.
- Whether the hot added memory can automatically go online depends on the VM OS logic. You can manually bring the memory online or configure the udev rules to automatically bring the memory online.
Procedure
VM XML Configuration
To use the memory hot add function, configure the maximum hot add memory size and reserved slot number, and configure the Guest NUMA topology when creating a VM.
For example, run the following command to configure 32 GB initial memory for a VM, reserve 256 slots, set the memory upper limit to 1 TB, and configure two NUMA nodes:
<domain type='kvm'> <memory unit='GiB'>32</memory> <maxMemory slots='256' unit='GiB'>1024</maxMemory> <cpu mode='host-passthrough' check='none'> <topology sockets='2' cores='2' threads='1'/> <numa> <cell id='0' cpus='0-1' memory='16' unit='GiB'/> <cell id='1' cpus='2-3' memory='16' unit='GiB'/> </numa> </cpu> ....
Note
In the preceding information, the value of slots in the maxMemory field indicates the reserved memory slots. The maximum value is 256. maxMemory indicates the maximum physical memory supported by the VM. For details about how to configure Guest NUMA, see "Configuring Guest NUMA."
Hot Adding and Bringing Memory Online
If the hot added memory needs to be automatically brought online, create the udev rules file /etc/udev/rules.d/99-hotplug-memory.rules in the VM as user root and define the udev rules in the file. The following is an example:
### automatically online hot-plugged memory ACTION=="add", SUBSYSTEM=="memory", ATTR{state}="online"Create a memory description XML file based on the size of the memory to be hot added and the Guest NUMA node of the VM.
For example, to hot add 1 GB memory to NUMA node0, run the following command:
<memory model='dimm'> <target> <size unit='MiB'>1024</size> <node>0</node> </target> </memory>Run the virsh attach-device command to hot add memory to the VM. In the command, openEulerVM indicates the VM name, memory.xml indicates the description file of the hot added memory, and --live indicates that the hot added memory takes effect online. You can also run the --config command to persist the hot added memory to the VM XML file.
### virsh attach-device openEulerVM memory.xml --live Note
Note
If you do not use the udev rules, you can use the root permission to manually bring the hot added memory online by running the following command:for i in `grep -l offline /sys/devices/system/memory/memory*/state` do echo online > $i done










