K3s Deployment Guide
What Is K3s?
K3s is a lightweight Kubernetes distribution that is optimized for edge computing and IoT scenarios. The K3s provides the following enhanced features:
- Packaged as a single binary file.
- Uses SQLite3-based lightweight storage backend as the default storage mechanism and supports etcd3, MySQL, and PostgreSQL.
- Encapsulated in a simple launcher that handles various complex TLS and options.
- Secure by default and has reasonable default values for lightweight environments.
- Batteries included, providing simple but powerful functions such as local storage providers, service load balancers, Helm controllers, and Traefik Ingress controllers.
- Encapsulates all operations of the Kubernetes control plane in a single binary file and process, capable of automating and managing complex cluster operations including certificate distribution.
- Minimizes external dependencies and requires only kernel and cgroup mounting.
Application Scenarios
K3s is applicable to the following scenarios:
- Edge computing
- IoT
- Continuous integration
- Development
- ARM
- Embedded Kubernetes
The resources required for running K3s are small. Therefore, K3s is also suitable for development and test scenarios. In these scenarios, K3s facilitates function verification and problem reproduction by shortening cluster startup time and reducing resources consumed by the cluster.
Deploying K3s
Step 1 Preparations
- Ensure that the host names of the server node and agent node are different.
You can run the hostnamectl set-hostname "host name" command to change the host name.

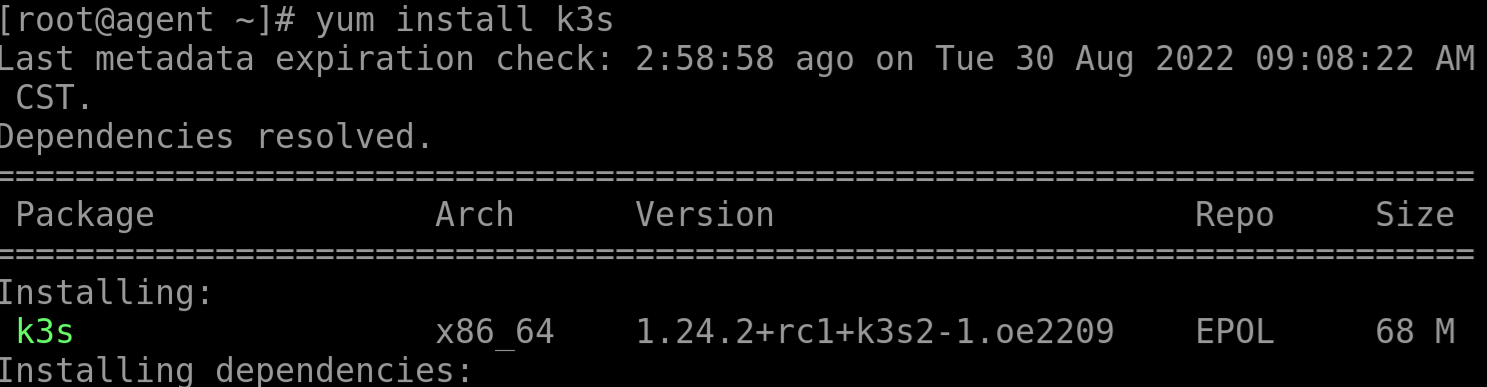
Install K3s on each node using Yum.
The K3s official website provides binary executable files of different architectures and the install.sh script for offline installation. The openEuler community migrates the compilation process of the binary file to the community and releases the compiled RPM package. You can run the
yumcommand to download and install K3s.
Step 2 Deploying the Server Node
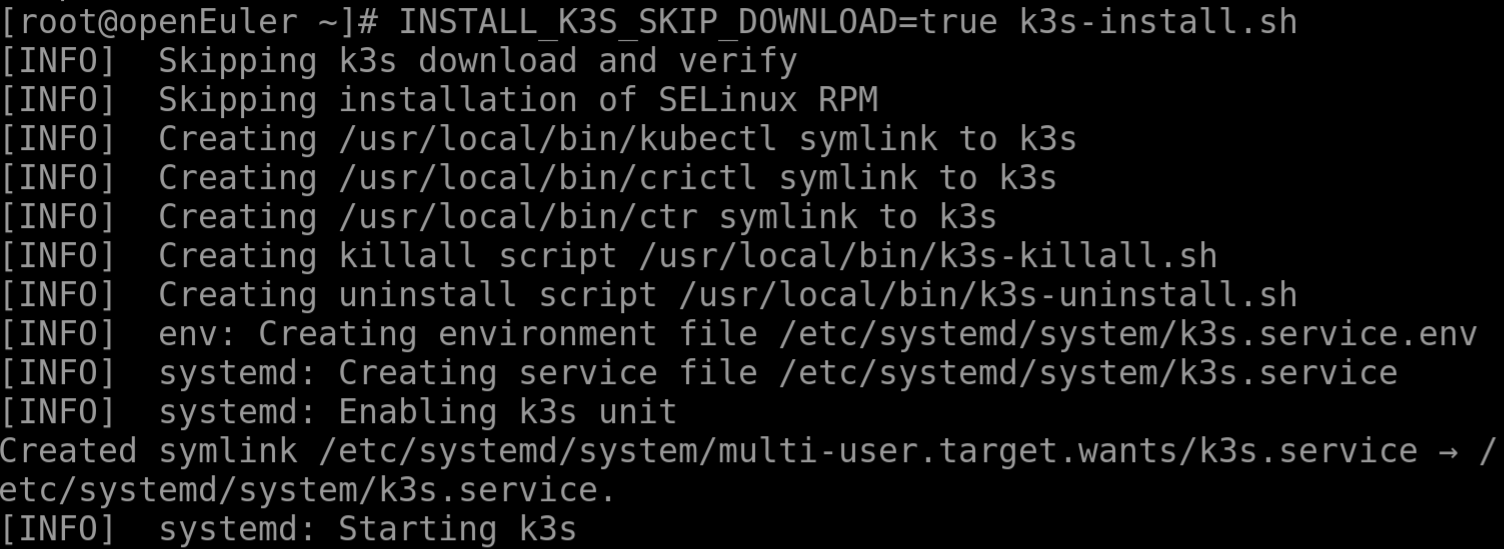
To install K3s on a single server, run the following command on the server node:
INSTALL_K3S_SKIP_DOWNLOAD=true k3s-install.sh
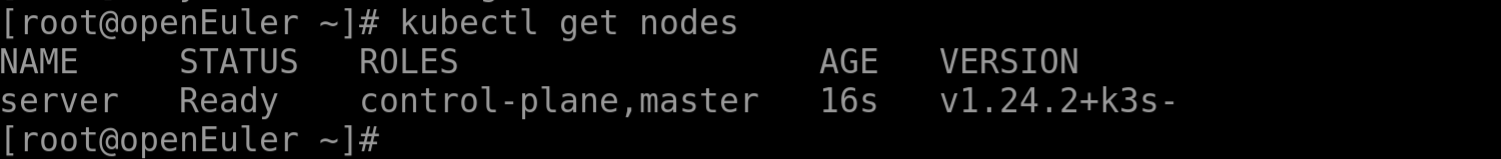
Step 3 Checking Server Deployment
Step 4 Deploying the Agent Node
Query the token value of the server node. The token is stored in the /var/lib/rancher/k3s/server/node-token file on the server node.
Note:
Only the second half of the token is used.

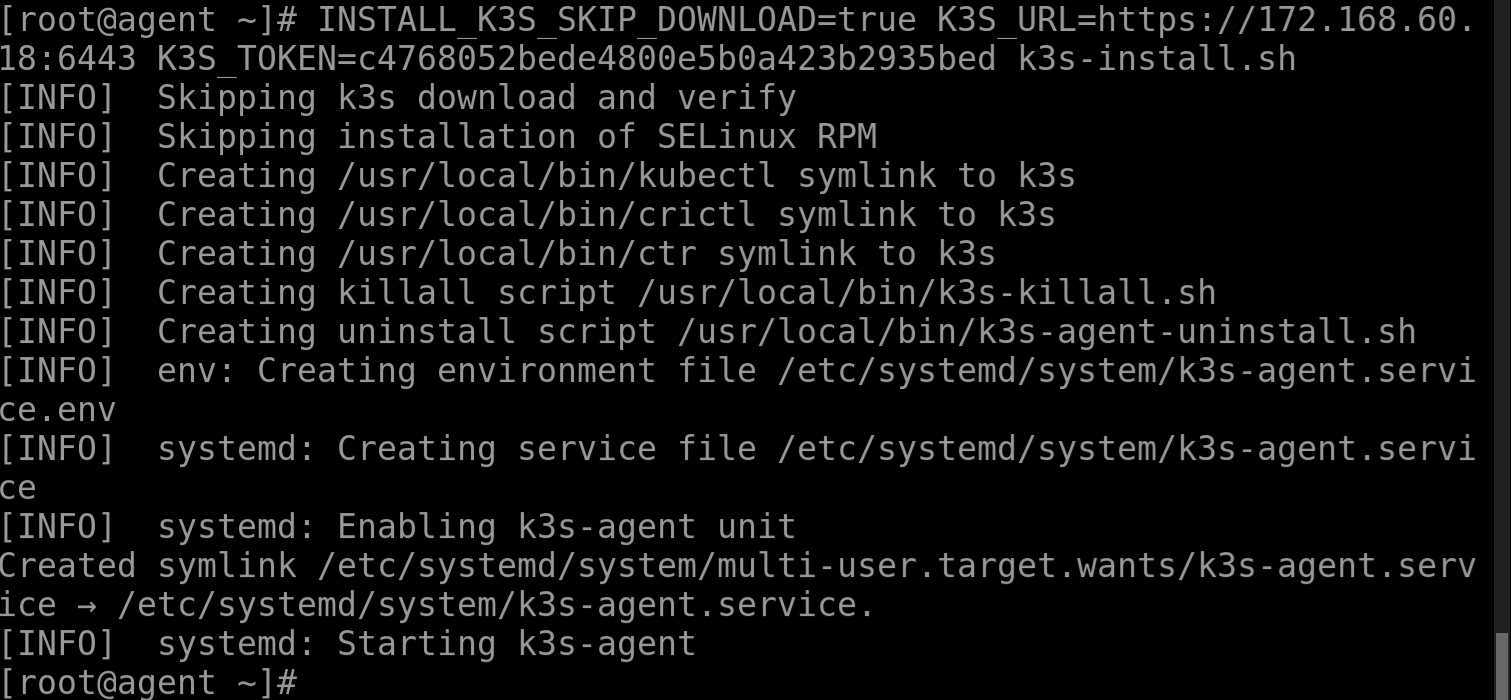
Add agents. Run the following command on each agent node:
INSTALL_K3S_SKIP_DOWNLOAD=true K3S_URL=https://myserver:6443 K3S_TOKEN=mynodetoken k3s-install.sh
Note:
Replace myserver with the IP address of the server or a valid DNS, and replace mynodetoken with the token of the server node.
Step 5 Checking Agent Deployment
After the installation is complete, run kubectl get nodes on the server node to check if the agent node is successfully registered.
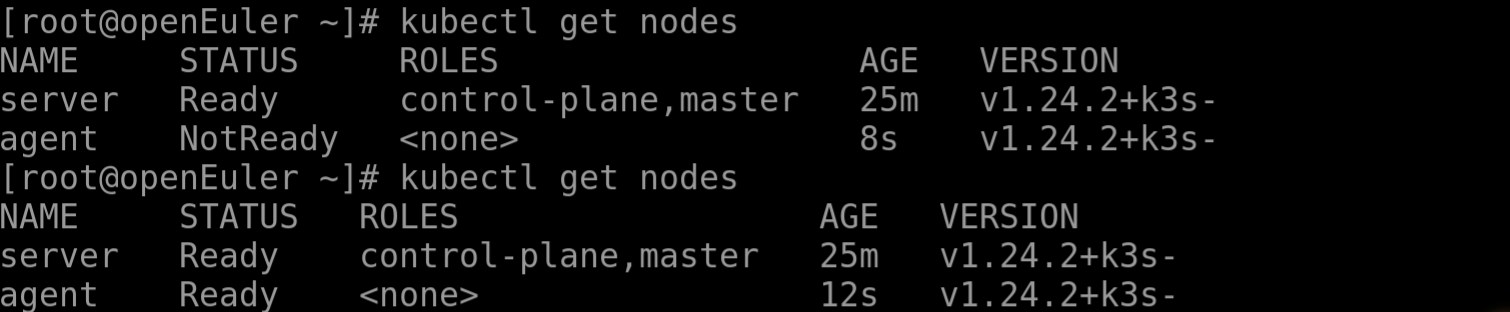
A basic K3S cluster is set up.
More
For details about how to use K3s, visit the K3s official website.










