FAQs
- FAQs
- Why Is the Memory Usage of the libvirtd Service Queried by Running the systemctl and top Commands Different?
- An Error Occurs When stripsize Is Set to 4 During RAID 0 Volume Configuration
- Failed to Compile MariaDB Using rpmbuild
- Failed to Start the SNTP Service Using the Default Configuration
- Installation Failure Caused by Software Package Conflict, File Conflict, or Missing Software Package
- Failed to Downgrade libiscsi
- Failed to Downgrade xfsprogs
- Failed to Downgrade elfutils
- CPython/Lib Detects CVE-2019-9674: Zip Bomb
- ReDoS Attack Occurs Due to Improper Use of glibc Regular Expressions
- An Error Is Reported When gdbm-devel Is Installed or Uninstalled During the Installation and Uninstallation of httpd-devel and apr-util-devel
- An rpmdb Error Is Reported When Running the yum or dnf Command After the System Is Rebooted
- Failed to Run
rpmrebuild -d /home/test filesystemto Rebuild the filesystem Package - An Error Is Reported When modprobe or insmod Is Executed With the -f Option
- Failed to Start the Nginx Service
- Failed to Install the OS on a Drive in a Soft RAID Array
Why Is the Memory Usage of the libvirtd Service Queried by Running the systemctl and top Commands Different?
Symptom
The output of the systemctl and systemd-cgtop commands shows that the libvirtd service occupies more than 1.5 GB memory, but the output of the top command shows that the libvirtd service occupies about 70 MB memory.
Possible Cause
The memory displayed in the services (including systemctl and systemd-cgtop) managed by systemd can be obtained from memory.usage_in_bytes in Cgroup. Running the top command is to query the memory information in the /proc directory. The query results are different because the statistical method varies.
Generally, the memory used by service processes has the following types:
- anon_rss: anonymous pages in user mode address spaces, for example, memory allocated by calling the malloc function or the mmap function with configured MAP_ANONYMOUS. When the system memory is insufficient, this type of memory can be swapped by the kernel.
- file_rss: mapped pages in user mode address spaces, including map file (such as mmap of a specified file) and map tmpfs (such as IPC shared memory). When the system memory is insufficient, the kernel can reclaim these pages. Data may need to be synchronized between the kernel and map file before reclamation.
- file_cache: file cache (page in page cache of disk file), which is generated when a file is read or written. When the system memory is insufficient, the kernel can reclaim these pages. Data may need to be synchronized between the kernel and map file before reclamation.
- buffer pages: belongs to page cache, for example, cache generated when block device files are read.
anon_rss and file_rss belong to the resident set size (RSS) of processes, and file_cache and buffer pages belong to page cache. In brief:
RSS in the output of the top command = anon_rss + file_rss; Shared memory (SHR) = file_rss
memory.usage_in_bytes in Cgroup = cache + RSS + swap
In conclusion, the definition of memory usage obtained by running the systemd command is different from that obtained by running the top command. Therefore, the query results are different.
An Error Occurs When stripsize Is Set to 4 During RAID 0 Volume Configuration
Symptom
An error occurs when the stripsize parameter is set to 4 during RAID 0 volume configuration.
Possible Cause
The 64 KB page table can be enabled only in the scenario where stripsize is set to 64.
Solution
You do not need to modify the configuration file. When running the lvcreate command on openEuler, set stripesize to 64 because the minimum supported stripe size is 64 KB.
Failed to Compile MariaDB Using rpmbuild
Symptom
When you log in to the system as user root and run the rpmbuild command to compile the MariaDB source code, the compilation fails and the following information is displayed:
+ echo 'mysql can'\''t run test as root'
mysql can't run test as root
+ exit 1
Possible Cause
The MariaDB does not allow user root to execute test cases. However, test cases are automatically executed during compilation. As a result, the compilation process is blocked.
Solution
Use a text editor, such as vi, to modify the value of the runtest variable in the mariadb.spec file.
Before the modification:
%global runtest 1
After the modification:
%global runtest 0
The modification disables the function of executing test cases during compilation, which does not affect the compilation and the RPM package content after compilation.
Failed to Start the SNTP Service Using the Default Configuration
Symptom
The SNTP service fails to be started with the default configuration.
Possible Cause
The domain name of the NTP server is not added to the default configuration.
Solution
Modify the /etc/sysconfig/sntp file and add the domain name of the NTP server in China: 0.generic.pool.ntp.org.
Installation Failure Caused by Software Package Conflict, File Conflict, or Missing Software Package
Symptom
Software package conflict, file conflict, or missing software packages may occur during software package installation. As a result, the upgrade is interrupted and the installation fails. The error information about software package conflict, file conflict, and missing software packages is as follows:
The following is an example of software package conflict error information (the conflict between libev-libevent-devel-4.24-11.oe1.aarch64 and libevent-devel-2.1.11-2.oe1.aarch64 is used as an example):
package libev-libevent-devel-4.24-11.oe1.aarch64 conflicts with libevent-devel provided by libevent-devel-2.1.11-2.oe1.aarch64
- cannot install the best candidate for the job
- conflicting requests
The following is an example of file conflict error information (the /usr/bin/containerd file conflict is used as an example):
Error: Transaction test error:
file /usr/bin/containerd from install of containerd-1.2.0-101.oe1.aarch64 conflicts with file from package docker-engine-18.09.0-100.aarch64
file /usr/bin/containerd-shim from install of containerd-1.2.0-101.oe1.aarch64 conflicts with file from package docker-engine-18.09.0-100.aarch64
The following is an example of the error message indicating that the blivet-data software package is missing:
Error:
Problem: cannot install both blivet-data-1:3.1.1-6.oe1.noarch and blivet-data-1:3.1.1-5.noarch
- package python2-blivet-1:3.1.1-5.noarch requires blivet-data = 1:3.1.1-5, but none of the providers can be installed
- cannot install the best update candidate for package blivet-data-1:3.1.1-5.noarch
- problem with installed package python2-blivet-1:3.1.1-5.noarch(try to add '--allowerasing' to command line to replace conflicting packages or '--skip-broken' to skip uninstallable packages or '--nobest' to use not only best candidate packages)
Possible Cause
- In the software packages provided by openEuler, some software packages have different names but the same functions. As a result, the software packages cannot be installed at the same time.
- In the software packages provided by openEuler, some software packages have different names but the same functions. As a result, the files after installation are the same, causing file conflict.
- Some software packages are depended on by other software packages before the upgrade. After the software packages are upgraded, the software packages that depend on them may fail to be installed due to lack of software packages.
Solution
If a software package conflict occurs, perform the following steps (the software package conflict in "Symptom" is used as an example):
According to the error message displayed during the installation, the software package that conflicts with the to-be-installed software package libev-libevent-devel-4.24-11.oe1.aarch64 is libevent-devel-2.1.11-2.oe1.aarch64.
Run the dnf remove command to uninstall the software package that conflicts with the software package to be installed.
dnf remove libevent-devel-2.1.11-2.oe1.aarch64Perform the installation again.
If a file conflict occurs, perform the following steps (the file conflict in "Symptom" is used as an example):
According to the error message displayed during the installation, the names of the software packages that cause the file conflict are containerd-1.2.0-101.oe1.aarch64 and docker-engine-18.09.0-100.aarch64.
Record the names of the software packages that do not need to be installed. The following uses docker-engine-18.09.0-100.aarch64 as an example.
Run the dnf remove command to uninstall the software package that does not need to be installed.
dnf remove docker-engine-18.09.0-100.aarch64Perform the installation again.
If a software package is missing, perform the following steps (the missed software package in "Symptom" is used as an example):
Determine the name of the software package to be upgraded (blivet-data-1:3.1.1-5.noarch) and the name of the dependent software package (python2-blivet-1:3.1.1-5.noarch) based on the error information displayed during the upgrade.
Run the dnf remove command to uninstall the software package that depends on the upgrade package or add the --allowerasing parameter when upgrading the software package.
Run the dnf remove command to uninstall the software package that depends on the blivet-data-1:3.1.1-5.noarch software package.
dnf remove python2-blivet-1:3.1.1-5.noarchAdd the --allowerasing parameter when upgrading the software package.
yum update blivet-data-1:3.1.1-5.noarch -y --allowerasing
Perform the upgrade again.
Installing Conflicting Instances
A file conflict occurs.
The python3-edk2-devel.noarch file conflicts with the build.noarch file due to duplicate file names.
$ yum install python3-edk2-devel.noarch build.noarch ... Error: Transaction test error: file /usr/bin/build conflicts between attempted installs of python3-edk2-devel-202002-3.oe1.noarch and build-20191114-324.4.oe1.noarch
Failed to Downgrade libiscsi
Symptom
libiscsi-1.19.4 or later fails to be downgraded to libiscsi-1.19.3 or earlier.
Error:
Problem: problem with installed package libiscsi-utils-1.19.0-4.oe1.x86_64
- package libiscsi-utils-1.19.0-4.oe1.x86_64 requires libiscsi(x86-64) = 1.19.0-4.oe1, but none of the providers can be installed
- cannot install both libiscsi-1.19.0-3.oe1.x86_64 and libiscsi-1.19.0-4.oe1.x86_64
- cannot install both libiscsi-1.19.0-4.oe1.x86_64 and libiscsi-1.19.0-3.oe1.x86_64
- conflicting requests
(try to add '--allowerasing' to command line to replace conflicting packages or '--skip-broken' to skip uninstallable packages or '--nobest' to use not only best candidate packages)
Possible Cause
In libiscsi-1.19.3 or earlier, binary files named iscsi-xxx are packed into the main package libiscsi. However, these binary files introduce improper dependency CUnit. To solve this problem, in libiscsi-1.19.4, these binary files are separated into the libiscsi-utils subpackage. The main package is weakly dependent on the subpackage. You can integrate or uninstall the subpackage during image building based on product requirements. If the subpackage is not integrated or is uninstalled, the functions of the libiscsi main package are not affected. When libiscsi-1.19.4 or later is downgraded to libiscsi-1.19.3 or earlier and the libiscsi-utils subpackage is installed in the system, because libiscsi-1.19.3 or earlier does not contain libiscsi-utils, libiscsi-utils will fail to be downgraded. Due to the fact that libiscsi-utils depends on the libiscsi main package before the downgrade, a dependency problem occurs and the libiscsi downgrade fails.
Solution
Run the following command to uninstall the libiscsi-utils subpackage and then perform the downgrade:
yum remove libiscsi-utils
Failed to Downgrade xfsprogs
Symptom
xfsprogs-5.6.0-2 or later fails to be downgraded to xfsprogs-5.6.0-1 or earlier.
Error:
Problem: problem with installed package xfsprogs-xfs_scrub-5.6.0-2.oe1.x86_64
- package xfsprogs-xfs_scrub-5.6.0-2.oe1.x86_64 requires xfsprogs = 5.6.0-2.oe1, but none of the providers can be installed
- cannot install both xfsprogs-5.6.0-1.oe1.x86_64 and xfsprogs-5.6.0-2.oe1.x86_64
- cannot install both xfsprogs-5.6.0-2.oe1.x86_64 and xfsprogs-5.6.0-1.oe1.x86_64
- conflicting requests
Possible Cause
In xfsprogs-5.6.0-2, to reduce improper dependencies of the xfsprogs main package and separate experimental commands from the main package, the xfs_scrub* commands are separated into the xfsprogs-xfs_scrub subpackage. The xfsprogs main package is weakly dependent on the xfsprogs-xfs_scrub sub-package. You can integrate or uninstall the subpackage during image creation based on product requirements. If the subpackage is not integrated or is uninstalled, the functions of the xfsprogs main package are not affected.
When xfsprogs-5.6.0-2 or later is downgraded to xfsprogs-5.6.0-1 or earlier and the xfsprogs-xfs_scrub subpackage is installed in the system, because xfsprogs-5.6.0-1 or earlier does not contain xfsprogs-xfs_scrub, xfsprogs-xfs_scrub will fail to be downgraded. Due to the fact that xfsprogs-xfs_scrub depends on the xfsprogs main package before the downgrade, a dependency problem occurs and the xfsprogs downgrade fails.
Solution
Run the following command to uninstall the xfsprogs-xfs_scrub subpackage and then perform the downgrade:
yum remove xfsprogs-xfs_scrub
Failed to Downgrade elfutils
Symptom
The dependency is missing. As a result, elfutils failed to be downgraded.
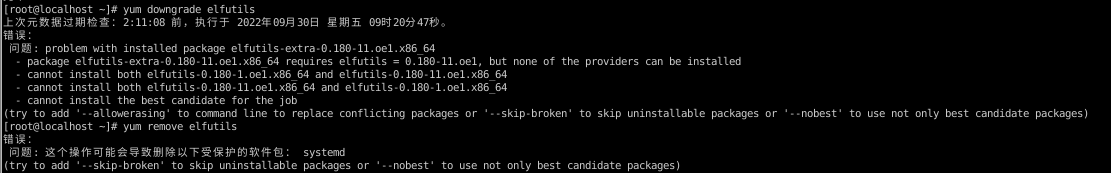
Possible Cause
22.03-LTS, 22.03-LTS-Next: elfutils-0.185-12
master: elfutils-0.187-7
20.03-LTS-SP1: elfutils-0.180-9
In the preceding versions, the eu-objdump, eu-readelf, and eu-nm commands provided by the elfutils main package are split into the elfutils-extra subpackage. When elfutils-extra has been installed in the system and elfutils is downgraded, because an earlier version (such as the version of an earlier branch) cannot provide the corresponding elfutils-extra package, the elfutils-extra subpackage is not downgraded. However, the elfutils-extra subpackage depends on the elfutils package before the downgrade. As a result, the dependency problem cannot be resolved, and the elfutils subpackage fails to be downgraded.
Solution
Run the following command to uninstall the elfutils-extra subpackage and then perform the downgrade:
yum remove -y elfutils-extra
CPython/Lib Detects CVE-2019-9674: Zip Bomb
Symptom
Lib/zipfile.py in Python 3.7.2 or earlier allows remote attackers to create DoS requests using zip bombs, resulting in high resource consumption.
Possible Cause
Remote attackers use zip bombs to cause denial of service, affecting target system services or even crashing the system. A zip bomb is a zip file with a high compression ratio. It may be several MB or dozens of MB in size. However, after decompression, a large amount of data is generated, consuming a large amount of resources.
Solution
Add the alarm information to zipfile at https://github.com/python/cpython/blob/3.7/Doc/library/zipfile.rst.
ReDoS Attack Occurs Due to Improper Use of glibc Regular Expressions
Symptom
The regcomp/regexec interface of glibc is used for programming, or the glibc regular expressions, such as grep/sed, are used in shell commands. Improper regular expressions or inputs cause ReDoS attacks (CVE-2019-9192/CVE-2018-28796). The typical regular expression pattern is the combination of the"reverse reference (\1)" with the "asterisk (*)" (zero match or multiple matches), "plus sign (+)" (one match or multiple matches), or "{m,n}" (minimum match: m; maximum match: n); or the combination of ultra-long character strings with regular expressions. The following is an example:
$ echo D | grep -E "$(printf '(\0|)(\\1\\1)*')"Segmentation fault (core dumped)
$ grep -E "$(printf '(|)(\\1\\1)*')"
Segmentation fault (core dumped)
$ echo A | sed '/\(\)\(\1\1\)*/p'
Segmentation fault (core dumped)
$ time python -c 'print "a"*40000' | grep -E "a{1,32767}"
Segmentation fault (core dumped)
$ time python -c 'print "a"*40900' | grep -E "(a)\\1"
Segmentation fault (core dumped)
Possible Cause
A core dump occurs on the process that uses the regular expression. The glibc regular expression is implemented using the NFA/DFA hybrid algorithm. The internal principle is to use a greedy algorithm for recursive query to match as many character strings as possible. The greedy algorithm causes the ReDoS attack when processing the recursive regular expression.
Solution
Strict permission control is required to reduce the attack surface.
Ensure that the regular expression is correct. Do not enter an invalid regular expression or a combination of ultra-long character strings with regular expressions (references or asterisks) that may trigger infinite recursion.
# ()(\1\1)* # "a"*400000After a user program detects a process exception, the user program can restart the process to restore services, improving program reliability.
An Error Is Reported When gdbm-devel Is Installed or Uninstalled During the Installation and Uninstallation of httpd-devel and apr-util-devel
Symptom
- An error is reported when gdbm-devel-1.18.1-1 is installed or uninstalled.
- After the error is rectified, gdbm and gdbm-devel are upgraded to the 1.18.1-2 version. However, the default version of gdbm-devel is still 1.18.1-1 when httpd-devel and apr-util-devel (dependent on gdbm-devel) are installed. As a result, the error persists.
Possible Cause
The gdbm-devel-1.18.1-1 package does not contain the help package that provides
info. As a result, the help package cannot be introduced when gdbm-devel is installed independently, and the following alarm information is displayed:install-info: No such file or directory for /usr/share/info/gdbm.info.gzBy default, the gdbm-1.18.1-1 main package is installed in the system, but the gdbm-devel package is not installed. The software packages depending on gdbm-devel still match the version of the gdbm main package and install gdbm-devel-1.18.1-1. As a result, the error persists.
Solution
- Install gdbm-1.18.1-2 to upgrade gdbm. The error is rectified.
- Upgrade gdbm, and then install gdbm-devel to make it depend on the gdbm of the later version. The error is rectified.
An rpmdb Error Is Reported When Running the yum or dnf Command After the System Is Rebooted
Symptom
- After the system is rebooted, an error is reported when running an RPM-related command
yumordnfas follows:
error: db5 error(-30973) from dbenv->open: BDB0087 DB_RUNRECOVERY: Fatal error, run database recovery
error: cannot open Packages index using db5 - (-30973)
error: cannot open Packages database in /var/lib/rpm
Error: Error: rpmdb open failed
Possible Cause
- During an installation or upgrade, read and write operations are performed on the /var/lib/rpm/__db.00* file. If an unexpected interruption occurs, such as forced power-off, drive space full, or
kill -9, the _db file will be damaged. An error will be reported when adnforyumcommand is executed.
Solution
Step 1 Run the kill -9 command to terminate all running RPM-related commands.
Step 2 Delete all /var/lib/rpm/__db.00* files.
Step 3 Run the rpmdb --rebuilddb command to rebuild the RPM database.
Failed to Run rpmrebuild -d /home/test filesystem to Rebuild the filesystem Package
Symptom
Failed to run the rpmrebuild --comment-missing=y --keep-perm -b -d /home/test filesystem-3.16-3.oe1.aarch64 command to rebuild the filesystem package. The following information is displayed:
/usr/lib/rpmrebuild/rpmrebuild.sh:Error:(RpmBuild) Package 'filesystem-3.16-3.oe1.aarch64' build failed.
/usr/lib/rpmrebuild/rpmrebuild.sh:Error: RpmBuild
Possible Cause
The software package creates the directory in the %pretrans -p phase, and modify the diretory in the %ghost phase. If you create a file or diretory in the diretory and use rpmrebuild to build the package, the created file or directory will be included in the package.
The root cause of the symptom is that filesystem creates the /proc diretory in the %pretrans phase and modifies the directory in the %ghost phase, but some small processes are dynamically created during system running. As a result, rpmrebuild cannot include the processes in the package because they are not files or diretories and fails to rebuild the package.
Solution
Do not use rpmrebuild to rebuild the filesystem package.
An Error Is Reported When modprobe or insmod Is Executed With the -f Option
Symptom
An error is reported when modprobe -f <mod> or insmod -f <mod>.ko.xz is executed. For example, when insmod -f xfs.ko.xz is executed, error message modprobe: ERROR: could not insert 'xfs': Key was rejected by service is displayed.
Up till now (2022.09.20, kmod v30), this issue has not been fixed by the kmod community.Linux v5.17 b1ae6dc introduced support for compressed kernel modules, which is not supported by kmod.
Possible Cause
modprobe and insmod use the finit_module() system call to load uncompressed ko files. For compressed ko files, kmod uses the init_module() system call to decompress them. init_module() does not take the ignore check flag. As a result, mod_verify_sig() is always executed by the kernel. the -f option of modprobe and insmod changes verification information about the ko file, resulting in verification failure of mod_verify_sig().
Solution
Do not use the -f option when running insmod or modprobe on compressed ko files.
Failed to Start the Nginx Service
Symptom
The Nginx service fails to be started, and the following error information is displayed:
systemctl status nginx.service --full
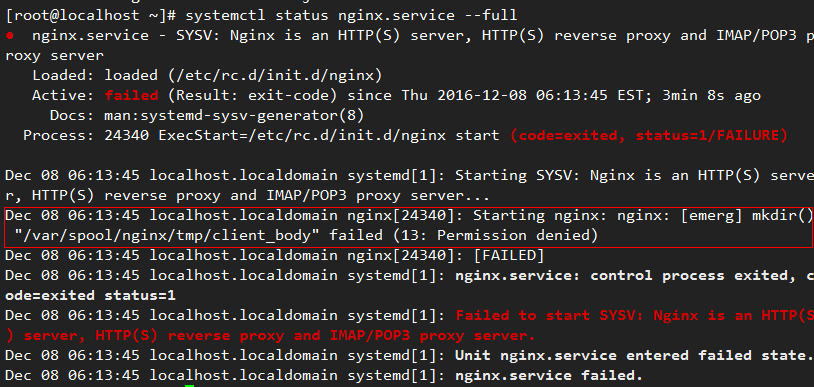
Possible Cause
The /var/spool/nginx/tmp/client_body directory fails to be created.
Solution
Manually create the related directories.
mkdir -p /var/spool/nginx/tmp/client_body
mkdir -p /var/spool/nginx/tmp/proxy
mkdir -p /var/spool/nginx/tmp/fastcgi
mkdir -p /usr/share/nginx/uwsgi_temp
mkdir -p /usr/share/nginx/scgi_temp
Failed to Install the OS on a Drive in a Soft RAID Array
Symptom
The drive used for OS installation is added to a soft RAID array. After the system is restarted, the OS fails to be installed on the drive.
Possible Cause
If a drive in a soft RAID array is used for OS installation, the RAID array must be formed on a small system so that the RAID information can be obtained on a large system. However, the soft RAID is not formed before the OS is installed, and the RAID information cannot be obtained. As a result, the OS fails to be installed.
Solution
Add boot parameters rd.md=1 and rd.auto=1 to enable detection and automatic formation of RAID arrays. This allows the RAID array to be automatically formed on the small system, which ensures that the RAID information can be obtained on the large system, thereby ensuring a normal OS installation.










