Using the Kunpeng Accelerator Engine (KAE)
- Using the Kunpeng Accelerator Engine (KAE)
Overview
Kunpeng Accelerator Engine (KAE) is a software acceleration library of openEuler, which provides hardware acceleration engine function on the Kunpeng 920 processor. It supports symmetric encryption, asymmetric encryption, and digital signature. It is ideal for accelerating SSL/TLS applications, reducing processor consumption and improving processor efficiency. In addition, users can quickly migrate existing services through the standard OpenSSL interface.
The KAE supports the following algorithms:
- Digest algorithm SM3, which supports asynchronous mode.
- Symmetric encryption algorithm SM4, which supports asynchronous, CTR, XTS, and CBC modes.
- Symmetric encryption algorithm AES, which supports asynchronous, ECB, CTR, XTS, and CBC modes.
- Asymmetric algorithm RSA, which supports asynchronous mode and key sizes 1024, 2048, 3072, and 4096.
- Key negotiation algorithm DH, which supports asynchronous mode and key sizes 768, 1024, 1536, 2048, 3072, and 4096.
Application Scenarios
The KAE applies to the following scenarios, as shown in Table 1.
Table 1 Application scenarios
Installing, Running, and Uninstalling the KAE
Installing the Accelerator Software Packages
Preparing for Installation
Environment Requirements
- The accelerator engine is enabled on TaiShan 200 servers.
NOTE:
- You need to import the accelerator license. For details, see section "License Management" in the TaiShan Rack Server iBMC (V500 or Later) User Guide.
- If the accelerator is used in the physical machine scenario, the SMMU must be disabled. For details, see the TaiShan 200 Server BIOS Parameter Reference.
- CPU: Kunpeng 920
- OS: openEuler-21.09-aarch64-dvd.iso
KAE Software Description
Table 2 RPM software packages of the KAE
Accelerator driver, including the uacce.ko, hisi_qm.ko, hisi_sec2.ko, and hisi_hpre.ko kernel modules. | |
Dependency: libwd RPM package. |
Installing the Accelerator Software Package
Prerequisites
The remote SSH login tool has been installed on the local PC.
The openEuler OS has been installed.
The RPM tool is running properly.
OpenSSL 1.1.1a or a later version has been installed.
You can run the following commands to query the version number of OpenSSL:
- openssl version
Procedure
Log in to the openEuler OS CLI as user root.
Create a directory for storing accelerator engine software packages.
Use SSH to copy all accelerator engine software packages to the created directory.
In the directory, run the rpm -ivh command to install the accelerator engine software packages.
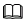 NOTE:
Install the libwd package first because the libkae package installation depends on the libwd package.
NOTE:
Install the libwd package first because the libkae package installation depends on the libwd package.rpm -ivh uacce*.rpm hisi*.rpm libwd-*.rpm libkae*.rpmVerifying... ################################# [100%] Preparing... ################################# [100%] checking installed modules uacce modules start to install Updating / installing... 1:uacce-1.2.10-4.oe1 ################################# [ 14%] uacce modules installed 2:libwd-1.2.10-3.oe1 ################################# [ 29%] 3:libkae-1.2.10-3.oe1 ################################# [ 43%] checking installed modules hisi_hpre modules start to install 4:hisi_hpre-1.2.10-4.oe1 ################################# [ 57%] hisi_hpre modules installed checking installed modules hisi_rde modules start to install 5:hisi_rde-1.2.10-4.oe1 ################################# [ 71%] hisi_rde modules installed checking installed modules hisi_sec2 modules start to install 6:hisi_sec2-1.2.10-4.oe1 ################################# [ 86%] hisi_sec2 modules installed checking installed modules hisi_zip modules start to install 7:hisi_zip-1.2.10-4.oe1 ################################# [100%] hisi_zip modules installedRun the rpm -qa command to check whether the accelerator software packages have been installed successfully. Run the rpm -ql command to check whether files in the software packages are correct. The following is an example:
rpm -qa|grep -E "hisi|uacce|libwd|libkae"hisi_rde-1.2.10-4.oe1.aarch64 hisi_sec2-1.2.10-4.oe1.aarch64 libkae-1.2.10-3.oe1.aarch64 hisi_hpre-1.2.10-4.oe1.aarch64 uacce-1.2.10-4.oe1.aarch64 libwd-1.2.10-3.oe1.aarch64 hisi_zip-1.2.10-4.oe1.aarch64rpm -ql uacce hisi* libwd* libkae/lib/modules/4.19.90-2003.4.0.0036.oe1.aarch64/extra/hisi_qm.ko /lib/modules/4.19.90-2003.4.0.0036.oe1.aarch64/extra/uacce.ko /etc/modprobe.d/hisi_hpre.conf /lib/modules/4.19.90-2003.4.0.0036.oe1.aarch64/extra/hisi_hpre.ko /etc/modprobe.d/hisi_rde.conf /lib/modules/4.19.90-2003.4.0.0036.oe1.aarch64/extra/hisi_rde.ko /etc/modprobe.d/hisi_sec2.conf /lib/modules/4.19.90-2003.4.0.0036.oe1.aarch64/extra/hisi_sec2.ko /etc/modprobe.d/hisi_zip.conf /lib/modules/4.19.90-2003.4.0.0036.oe1.aarch64/extra/hisi_zip.ko /usr/include/warpdrive/config.h /usr/include/warpdrive/include/uacce.h /usr/include/warpdrive/smm.h /usr/include/warpdrive/wd.h /usr/include/warpdrive/wd_bmm.h /usr/include/warpdrive/wd_cipher.h /usr/include/warpdrive/wd_comp.h /usr/include/warpdrive/wd_dh.h /usr/include/warpdrive/wd_digest.h /usr/include/warpdrive/wd_rsa.h /usr/lib64/libwd.so.1.2.10 /usr/local/lib/engines-1.1/libkae.so.1.2.10Restart the system or run commands to manually load the accelerator engine drivers to the kernel in sequence, and check whether the drivers are successfully loaded.
modprobe uacce lsmod | grep uacce modprobe hisi_qm lsmod | grep hisi_qm modprobe hisi_sec2 # Loads the hisi_sec2 driver to the kernel based on the configuration file in /etc/modprobe.d/hisi_sec2.conf. modprobe hisi_hpre # Loads the hisi_hpre driver to the kernel based on the configuration file in /etc/modprobe.d/hisi_hpre.conf.
Environment Variables Setup
Run the following command to export the environment variables (If you have specified the installation directory, set /usr/local to the actual one):
export OPENSSL_ENGINES=/usr/local/lib/engines-1.1
Post-Installation Check
Run the rpm -qa command to check whether the accelerator engine software packages are successfully installed.
If the command output contains software package name-version number-, the software packages are successfully installed. The following is an example:
rpm -qa|grep -E "hisi|uacce|libwd|libkae"
hisi_rde-1.2.10-4.oe1.aarch64
hisi_sec2-1.2.10-4.oe1.aarch64
libkae-1.2.10-3.oe1.aarch64
hisi_hpre-1.2.10-4.oe1.aarch64
uacce-1.2.10-4.oe1.aarch64
libwd-1.2.10-3.oe1.aarch64
hisi_zip-1.2.10-4.oe1.aarch64
Required Operations After Installation
Testing the OpenSSL Accelerator Engine
You can run the following commands to test some accelerator functions.
Use the OpenSSL software algorithm to test the RSA performance.
$ ./openssl speed -elapsed rsa2048 ... sign verify sign/s verify/s rsa 2048 bits 0.001384s 0.000035s 724.1 28365.8.Use the KAE to test the RSA performance.
$ ./openssl speed -elapsed -engine kae rsa2048 .... sign verify sign/s verify/s rsa 2048 bits 0.000355s 0.000022s 2819.0 45478.4
NOTE: After the KAE is used, the signature performance is improved from 724.1 sign/s to 2819 sign/s.
Use the OpenSSL software algorithm to test the asynchronous RSA performance.
$ ./openssl speed -elapsed -async_jobs 36 rsa2048 .... sign verify sign/s verify/s rsa 2048 bits 0.001318s 0.000032s 735.7 28555Use the KAE to test the asynchronous RSA performance.
$ ./openssl speed -engine kae -elapsed -async_jobs 36 rsa2048 .... sign verify sign/s verify/s rsa 2048 bits 0.000018s 0.000009s 54384.1 105317.0
NOTE: After the KAE is used, the asynchronous RSA signature performance is improved from 735.7 sign/s to 54384.1 sign/s.
Use the OpenSSL software algorithm to test the performance of the SM4 CBC mode.
$ ./openssl speed -elapsed -evp sm4-cbc You have chosen to measure elapsed time instead of user CPU time. .... Doing sm4-cbc for 3s on 10240 size blocks: 2196 sm4-cbc's in 3.00s .... type 51200 bytes 102400 bytes1048576 bytes2097152 bytes4194304 bytes8388608 bytes sm4-cbc 82312.53k 85196.80k 85284.18k 85000.85k 85284.18k 85261.26kUse the KAE to test the SM4 CBC mode performance.
$ ./openssl speed -elapsed -engine kae -evp sm4-cbc engine "kae" set. You have chosen to measure elapsed time instead of user CPU time. ... Doing sm4-cbc for 3s on 1048576 size blocks: 11409 sm4-cbc's in 3.00s ... type 51200 bytes 102400 bytes1048576 bytes2097152 bytes4194304 bytes8388608 bytes sm4-cbc 383317.33k 389427.20k 395313.15k 392954.73k 394264.58k 394264.58k
NOTE: After the KAE is used, the SM4 CBC mode performance is improved from 82312.53 kbit/s to 383317.33 kbit/s when the input data block size is 8 MB.
Use the OpenSSL software algorithm to test the SM3 mode performance.
$ ./openssl speed -elapsed -evp sm3 You have chosen to measure elapsed time instead of user CPU time. Doing sm3 for 3s on 102400 size blocks: 1536 sm3's in 3.00s .... type 51200 bytes 102400 bytes1048576 bytes2097152 bytes4194304 bytes8388608 bytes sm3 50568.53k 52428.80k 52428.80k 52428.80k 52428.80k 52428.80kUse the KAE to test the SM3 mode performance.
$ ./openssl speed -elapsed -engine kae -evp sm3 engine "kae" set. You have chosen to measure elapsed time instead of user CPU time. Doing sm3 for 3s on 102400 size blocks: 19540 sm3's in 3.00s .... type 51200 bytes 102400 bytes 1048576 bytes 2097152 bytes 4194304 bytes 8388608 bytes sm3 648243.20k 666965.33k 677030.57k 678778.20k 676681.05k 668292.44k
NOTE: After the KAE is used, the SM3 algorithm performance is improved from 52428.80 kbit/s to 668292.44 kbit/s when the input data block size is 8 MB.
Use the OpenSSL software algorithm to test the asynchronous performance of the AES algorithm in CBC mode.
$ ./openssl speed -elapsed -evp aes-128-cbc -async_jobs 4 You have chosen to measure elapsed time instead of user CPU time. Doing aes-128-cbc for 3s on 51200 size blocks: 65773 aes-128-cbc's in 3.00s Doing aes-128-cbc for 3s on 102400 size blocks: 32910 aes-128-cbc's in 3.00s .... type 51200 bytes 102400 bytes1048576 bytes2097152 bytes4194304 bytes8388608 bytes aes-128-cbc 1122525.87k 1123328.00k 1120578.22k 1121277.27k 1119879.17k 1115684.86kUse the KEA engine to test the asynchronous performance of the AES algorithm in CBC mode.
$ ./openssl speed -elapsed -evp aes-128-cbc -async_jobs 4 -engine kae engine "kae" set. You have chosen to measure elapsed time instead of user CPU time. Doing aes-128-cbc for 3s on 51200 size blocks: 219553 aes-128-cbc's in 3.00s Doing aes-128-cbc for 3s on 102400 size blocks: 117093 aes-128-cbc's in 3.00s .... type 51200 bytes 102400 bytes1048576 bytes2097152 bytes4194304 bytes8388608 bytes aes-128-cbc 3747037.87k 3996774.40k 1189085.18k 1196774.74k 1196979.11k 1199570.94k
NOTE:
- The AES algorithm supports only asynchronous mode when the data length is 256 KB or less.
- After the KAE is used, the AES algorithm performance is improved from 1123328.00 kbit/s to 3996774.40 kbit/s when the input data block size is 100 KB.
Upgrading the Accelerator Software Packages
Scenario
You can run the rpm -Uvh command to upgrade the accelerator software.
Procedure
Download the latest accelerator engine software packages from the openEuler community.
Use SSH to log in to the Linux CLI as user root.
Save the downloaded software packages to a directory.
In the directory, run the rpm -Uvh command to upgrade the accelerator driver package and engine library package. The following is an example:
The command and output are as follows:
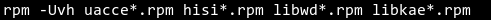
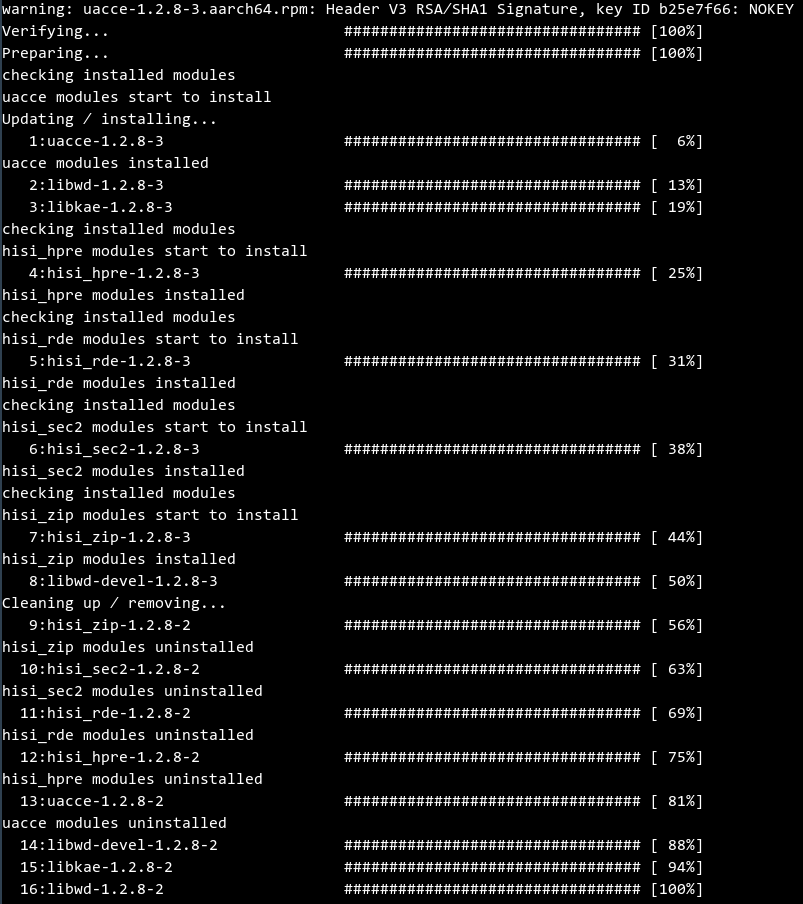
Run the rpm -qa command to check whether the upgrade is successful. Ensure that the queried version is the latest version.

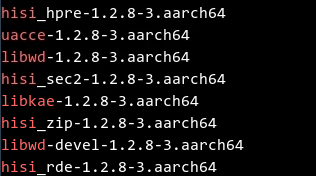
Restart the system or run the following commands to manually uninstall the drivers of the earlier version, load the drivers of the latest version, and check whether the new drivers are successfully loaded.
# Uninstall the existing drivers. $ lsmod | grep uacce uacce 262144 3 hisi_hpre,hisi_sec2,hisi_qm $ $ rmmod hisi_hpre $ rmmod hisi_sec2 $ rmmod hisi_qm $ rmmod uacce $ lsmod | grep uacce $ # Load the new drivers. $ modprobe uacce $ modprobe hisi_qm $ modprobe hisi_sec2 # Loads the hisi_sec2 driver to the kernel based on the configuration file in /etc/modprobe.d/hisi_sec2.conf. $ modprobe hisi_hpre # Loads the hisi_hpre driver to the kernel based on the configuration file in /etc/modprobe.d/hisi_hpre.conf. $ lsmod | grep uacce uacce 36864 3 hisi_sec2,hisi_qm,hisi_hpre
Uninstalling the Accelerator Software Packages
Scenario
You do not need the accelerator engine software or you want to install a new one.
Procedure
Use SSH to log in to the Linux CLI as user root.
Restart the system or run commands to manually uninstall the accelerator drivers loaded to the kernel, and check whether the drivers are successfully uninstalled.
# lsmod | grep uacce uacce 36864 3 hisi_sec2,hisi_qm,hisi_hpre # rmmod hisi_hpre # rmmod hisi_sec2 # rmmod hisi_qm # rmmod uacce # lsmod | grep uacce #Run the rpm -e command to uninstall the accelerator engine software packages. The following is an example:
 NOTE:
Due to the dependency relationships, the libkae package must be uninstalled before the libwd package.
NOTE:
Due to the dependency relationships, the libkae package must be uninstalled before the libwd package.
Run the rpm -qa |grep command to check whether the uninstallation is successful.

Querying Logs
Table 3 lists log information related to the accelerator engine.
Table 3 Log information
By default, the log level of the OpenSSL engine log is error. To set the log level, perform the following procedure: | ||
Acceleration Engine Application
NOTE: If you have not purchased the engine license, you are advised not to use the KAE to invoke the corresponding algorithms. Otherwise, the performance of the OpenSSL encryption algorithm may be affected.
Example Code for the KAE
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
/* OpenSSL headers */
#include <openssl/bio.h>
#include <openssl/ssl.h>
#include <openssl/err.h>
#include <openssl/engine.h>
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
/* Initializing OpenSSL */
SSL_load_error_strings();
ERR_load_BIO_strings();
OpenSSL_add_all_algorithms();
/*You can use ENGINE_by_id Function to get the handle of the Huawei Accelerator Engine*/
ENGINE *e = ENGINE_by_id("kae");
/* Enable the accelerator asynchronization function. This parameter is optional. The value 0 indicates disabled, and the value 1 indicates enabled. The asynchronous function is enabled by default. */
ENGINE_ctrl_cmd_string(e, "KAE_CMD_ENABLE_ASYNC", "1", 0)
ENGINE_init(e);
RSA*rsa=RSA_new_method(e);#Specify the engine for RSA encryption and decryption.
/*The user code*/
......
;
ENGINE_free(e);
;
}
Usage of the KAE in the OpenSSL Configuration File openssl.cnf
Create the openssl.cnf file and add the following configuration information to the file:
openssl_conf=openssl_def
[openssl_def]
engines=engine_section
[engine_section]
kae=kae_section
[kae_section]
engine_id=kae
dynamic_path=/usr/local/lib/engines-1.1/kae.so
KAE_CMD_ENABLE_ASYNC=1 #The value 0 indicates that the asynchronous function is disabled. The value 1 indicates that the asynchronous function is enabled. The asynchronous function is enabled by default.
default_algorithms=ALL
init=1
Export the environment variable OPENSSL_CONF.
export OPENSSL_CONF=/home/app/openssl.cnf #Path for storing the openssl.cnf file
The following is an example of the OpenSSL configuration file:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
/* OpenSSL headers */
#include <openssl/bio.h>
#include <openssl/ssl.h>
#include <openssl/err.h>
#include <openssl/engine.h>
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
/* Initializing OpenSSL */
SSL_load_error_strings();
ERR_load_BIO_strings();
#Load openssl configure
OPENSSL_init_crypto(OPENSSL_INIT_LOAD_CONFIG, NULL); OpenSSL_add_all_algorithms();
/*You can use ENGINE_by_id Function to get the handle of the Huawei Accelerator Engine*/
ENGINE *e = ENGINE_by_id("kae");
/*The user code*/
......
;
ENGINE_free(e);
;
}
Troubleshooting
Failed to Initialize the Accelerator Engine
Symptom
The accelerator engine is not completely loaded.
Solution
Check whether the accelerator drivers are loaded successfully. Specifically, run the lsmod command to check whether uacce.ko, qm.ko, sgl.ko, hisi_sec2.ko, hisi_hpre.ko, hisi_zip.ko, and hisi_rde.ko exist.
$ lsmod | grep uacce uacce 262144 2 hisi_hpre,hisi_qm,hisi_sec2,hisi_zip,hisi_rdeCheck whether the accelerator engine library exists in /usr/lib64 (directory for RPM installation) or /usr/local/lib (directory for source code installation) and the OpenSSL installation directory, and check whether the correct soft link is established.
$ ll /usr/local/lib/engines-1.1/ |grep kae # Check whether the KAE has been correctly installed and whether a soft link has been established. If yes, the displayed information is as follows: lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 22 Nov 12 02:33 kae.so -> kae.so.1.0.1 lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 22 Nov 12 02:33 kae.so.0 -> kae.so.1.0.1 -rwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 112632 May 25 2019 kae.so.1.0.1 $ $ ll /usr/lib64/ | grep libwd # Check whether libwd has been correctly installed and whether a soft link has been established. If yes, the displayed information is as follows: lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 14 Nov 12 02:33 libwd.so -> libwd.so.1.0.1 lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 14 Nov 12 02:33 libwd.so.0 -> libwd.so.1.0.1 -rwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 137120 May 25 2019 libwd.so.1.0.1 $Check whether the path of the OpenSSL engine library can be exported by running the export command.
$ echo $OPENSSL_ENGINES $ export OPENSSL_ENGINES=/usr/local/lib/engines-1.1 $ echo $OPENSSL_ENGINES /usr/local/lib/engines-1.1
Failed to Identify Accelerator Devices After the Acceleration Engine Is Installed
Symptom
After the acceleration engine is installed, the accelerator devices cannot be identified.
Solution
Check whether the device exists in the virtual file system. Normally, the following accelerator devices are displayed:
$ ls -al /sys/class/uacce/ total 0 lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 0 Nov 14 03:45 hisi_hpre-2 -> ../../devices/pci0000:78/0000:78:00.0/0000:79:00.0/uacce/hisi_hpre-2 lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 0 Nov 14 03:45 hisi_hpre-3 -> ../../devices/pci0000:b8/0000:b8:00.0/0000:b9:00.0/uacce/hisi_hpre-3 lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 0 Nov 17 22:09 hisi_rde-4 -> ../../devices/pci0000:78/0000:78:01.0/uacce/hisi_rde-4 lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 0 Nov 17 22:09 hisi_rde-5 -> ../../devices/pci0000:b8/0000:b8:01.0/uacce/hisi_rde-5 lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 0 Nov 14 08:39 hisi_sec-0 -> ../../devices/pci0000:74/0000:74:01.0/0000:76:00.0/uacce/hisi_sec-0 lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 0 Nov 14 08:39 hisi_sec-1 -> ../../devices/pci0000:b4/0000:b4:01.0/0000:b6:00.0/uacce/hisi_sec-1 lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 0 Nov 17 22:09 hisi_zip-6 -> ../../devices/pci0000:74/0000:74:00.0/0000:75:00.0/uacce/hisi_zip-6 lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 0 Nov 17 22:09 hisi_zip-7 -> ../../devices/pci0000:b4/0000:b4:00.0/0000:b5:00.0/uacce/hisi_zip-7If you want to use the HPRE device but the device is not found in 1, check whether the accelerator software is correctly installed by referring to Failed to Upgrade the Accelerator Drivers.
If the accelerator software is correctly installed, run the lspci command to check whether the physical device exists.
$ lspci | grep HPRE 79:00.0 Network and computing encryption device: Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. HiSilicon HPRE Engine (rev 21) b9:00.0 Network and computing encryption device: Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. HiSilicon HPRE Engine (rev 21) $ lspci | grep SEC 76:00.0 Network and computing encryption device: Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. HiSilicon SEC Engine (rev 21) b6:00.0 Network and computing encryption device: Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. HiSilicon SEC Engine (rev 21) $ lspci | grep RDE 78:01.0 RAID bus controller: Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. HiSilicon RDE Engine (rev 21) b8:01.0 RAID bus controller: Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. HiSilicon RDE Engine (rev 21) $ lspci | grep ZIP 75:00.0 Processing accelerators: Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. HiSilicon ZIP Engine (rev 21) b5:00.0 Processing accelerators: Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. HiSilicon ZIP Engine (rev 21) $If no physical device is found in 3, perform the following operations:
- Check whether the accelerator license has been imported. If no, import the accelerator license. For details, see "License Management" in the TaiShan Rack Server iBMC (V500 or Later) User Guide. After the accelerator license is imported, power off and restart the iBMC to enable the license.
- Check whether the iBMC and BIOS versions support the accelerator feature.
Failed to Upgrade the Accelerator Drivers
Symptom
After the accelerator drivers are upgraded, the driver version is not changed after the system is restarted.
Possible Cause
Before the accelerator drivers are upgraded, the system upgrades other driver packages. These driver packages may update the boot file system initramfs, and update the accelerator drivers to initramfs before upgrade. For example, if the NIC driver is updated or initramfs is manually updated, the system loads the accelerator drivers from initramfs first during restart.
Solution
After the accelerator drivers are upgraded, run the dracut --force command to update initramfs again.










