Installing and Running EulerLauncher on macOS
Preparations
Installing Homebrew
Homebrew is the software package manager for macOS, which provides many practical functions, such as installation, uninstallation, update, viewing, and search. It allows you to use a simple command to manage packages without considering dependencies and file paths.
On the macOS desktop, press Shift+Command+U to open the Utilities folder in Go and find Terminal.app.
Install Homebrew based on the network status.
Run the following command to install Homebrew:
/bin/bash -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/HEAD/install.sh)"Alternatively, run the following command to install Homebrew:
/bin/zsh -c "$(curl -fsSL https://gitee.com/cunkai/HomebrewCN/raw/master/Homebrew.sh)"Installing QEMU and Wget
EulerLauncher depends on QEMU to run on macOS, and image download depends on Wget. Homebrew can be used to easily download and manage such software. Run the following command to install QEMU and Wget:
brew install qemu
brew install wgetConfiguring the sudo Password-Free Permission
EulerLauncher depends on QEMU to run on macOS. To improve user network experience, vmnet framework of macOS is used to provide VM network capabilities. Currently, administrator permissions are required for using vmnet. When using the QEMU backend to create VMs with vmnet network devices, you need to enable the administrator permission. EulerLauncher automatically uses the sudo command to implement this process during startup. Therefore, you need to configure the sudo password-free permission for the current user. If you do not want to perform this configuration, please stop using EulerLauncher.
On the macOS desktop, press Shift+Command+U to open the Utilities folder in Go and find Terminal.app.
Enter
sudo visudoin the terminal to modify the sudo configuration file. Note that you may be required to enter the password in this step. Enter the password as prompted.Find and replace
%admin ALL=(ALL) ALLwith%admin ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: ALL.Press ESC and enter :wq to save the settings.
Installing EulerLauncher
EulerLauncher supports macOS Ventura for Apple Silicon and x86 architectures. Download the latest version of EulerLauncher for macOS and decompress it to the desired location.
The directory generated after the decompression contains the following files:
install.exe is the installation file, which is used to install the support files required by EulerLauncher to the specified location. EulerLauncher.dmg is the disk image of the main program.
This operation requires the
sudopermission. You need to configure the sudo password-free permission first.Install the support files. Double-click the install file and wait until the program execution is completed.
Configure EulerLauncher.
Check the locations of QEMU and Wget. The name of the QEMU binary file varies according to the architecture. Select the correct name (Apple Silicon: qemu-system-aarch64; Intel: qemu-system-x86_64) as required.
Shellwhich wget which qemu-system-{host_arch}Reference output:
shell/opt/homebrew/bin/wget /opt/homebrew/bin/qemu-system-aarch64Record the paths, which will be used in the following steps.
Open the eulerlauncher.conf file and configure it.
shellsudo vi /Library/Application\ Support/org.openeuler.eulerlauncher/eulerlauncher.confEulerLauncher configurations are as follows:
ini[default] log_dir = # Log file location (xxx.log) work_dir = # EulerLauncher working directory, which is used to store VM images and VM files. wget_dir = # Path of the Wget executable file. Set this parameter based on the previous step. qemu_dir = # Path of the QEMU executable file. Set this parameter based on the previous step. debug = True [vm] cpu_num = 1 # Number of CPUs of the VM. memory = 1024 #Memory size of the VM, in MB. Do not set this parameter to a value greater than 2048 for M1 users.Save the modifications and exit.
Install EulerLauncher.app.
Double-click EulerLauncher.dmg. In the displayed window, drag EulerLauncher.app to Applications to complete the installation. You can find EulerLauncher.app in applications.
Using EulerLauncher
Find EulerLauncher.app in applications and click to start the program.
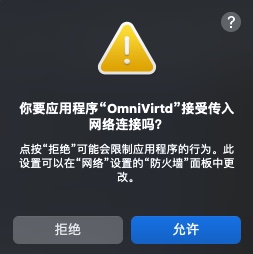
EulerLauncher needs to access the network. When the following dialog box is displayed, click Allow.
Currently, EulerLauncher can be accessed only in CLI mode. Open Terminal.app and use the CLI to perform operations.
Operations on Images
List available images.
Shelleulerlauncher imagesThere are two types of EulerLauncher images: remote images and local images. Only local images in the Ready state can be used to create VMs. Remote images can be used only after being downloaded. You can also load a downloaded local image to EulerLauncher. For details, see the following sections.
Download a remote image.
Shelleulerlauncher download-image 23.09 Downloading: 23.09, this might take a while, please check image status with "images" command.The image download request is an asynchronous request. The download is completed in the background. The time required depends on your network status. The overall image download process includes download, decompression, and format conversion. During the download, you can run the
imagecommand to view the download progress and image status at any time.Shelleulerlauncher imagesWhen the image status changes to Ready, the image is downloaded successfully. The image in the Ready state can be used to create VMs.
Shelleulerlauncher imagesLoad a local image.
Load a custom image or an image downloaded to the local host to EulerLauncher to create a custom VM.
Shelleulerlauncher load-image --path {image_file_path} IMAGE_NAMEThe supported image formats are xxx**.qcow2.xz** and xxx**.qcow2**.
Example:
Shelleulerlauncher load-image --path /opt/openEuler-23.09-x86_64.qcow2.xz 2309-load Loading: 2309-load, this might take a while, please check image status with "images" command.Load the openEuler-23.09-x86_64.qcow2.xz file in the /opt directory to the EulerLauncher system and name it 2309-load. Similar to the download command, the load command is also an asynchronous command. You need to run the image list command to query the image status until the image status is Ready. Compared with directly downloading an image, loading an image is much faster.
Shelleulerlauncher images ...... eulerlauncher images ......Delete an image.
Run the following command to delete an image from the EulerLauncher system:
Shelleulerlauncher delete-image 2309-load Image: 2309-load has been successfully deleted.
Operations on VMs
List VMs.
shelleulerlauncher list +----------+-----------+---------+---------------+ | Name | Image | State | IP | +----------+-----------+---------+---------------+ | test1 | 2309-load | Running | 172.22.57.220 | +----------+-----------+---------+---------------+ | test2 | 2309-load | Running | N/A | +----------+-----------+---------+---------------+If the VM IP address is N/A and the VM status is Running, the VM is newly created and the network configuration is not complete. Configuring the network takes several seconds. You can obtain the VM information again later.
Log in to a VM.
If an IP address has been assigned to a VM, you can run the
sshcommand to log in to the VM.Shellssh root@{instance_ip}If the official image provided by the openEuler community is used, the default username is root and the default password is openEuler12#$.
Create a VM.
Shelleulerlauncher launch --image {image_name} {instance_name}Use
--imageto specify an image and a VM name.Delete a VM.
Shelleulerlauncher delete-instance {instance_name}
Delete a specified VM based on the VM name.